Week 4
SEM and display advertising
You will learn about advertising opportunities within search engines, also called Search engine marketing (SEM) and Google Display advertising. You’ll learn best practices for creating an ad in search results or a display ad. You’ll finish the course understanding how to apply and improve display ads.
Dedication to study
-
Videos: 49 min
-
Leitura: 3 h 10 min
-
Teste: 1 Teste com avaliação
Learning Objectives
- Understand the benefits of SEM.
- Identify different types and structures of SEM ads.
- Apply search engine marketing.
- Understand fundamentals of Google Ads and targeting audiences.
- Understand different display advertising types.
- Define Google Display Ads best practices.
Content
- Understand engine marketing (SEM)
- Understand Google Ads
- Apply display advertising
- Review: Search engine marketing (SEM) and display advertising
- Course review: Attract and engage customers with digital marketing
1. Understand engine marketing (SEM)
Welcome to week 4
Video. Duration: 2 minutes
Welcome to this section, where we’ll explore the intricacies of understanding and applying search engine marketing and display advertising. Our focus here is on online paid advertising, covering a spectrum of ad types that span search engines, websites, and apps. Throughout this section, I’ll equip you with the knowledge you need to master advertising within Google’s search engine results, precisely targeting users searching for relevant products or services. Moreover, we’ll delve into advertising on external websites through the dynamic world of display networks. As a digital marketer or e-commerce analyst, online advertising is a vital component of your role, and mastering this skill is of paramount importance.
Our journey through this section begins with a comprehensive look at search engine marketing (SEM) and the underlying motivations behind marketers’ pursuit of it. SEM-based ads make their presence felt whenever someone initiates a search on a search engine. You’ll discover the intricacies of paid ads within the Google Search environment, navigating through the Google Ads platform. Expect to gain insight into the common formats Google Ads takes and a breakdown of the ad creation process, from setting up campaigns to choosing the right bidding strategies and audience targeting. You’ll also become well-versed in the diverse keyword match types at your disposal. Furthermore, I’ll demystify the ad auction, a pivotal process that dictates the positioning of ads in search results and the associated costs per click. This dynamic and pivotal operation occurs with every Google Ad-relevant search. We’ll culminate this section by delving into the art of crafting compelling ads.
Transitioning from SEM, we’ll explore display advertising—a form of online advertising characterized by visually appealing ads found across various web destinations. We’ll zoom in on a specific display ad type known as the responsive display ad. In addition to in-depth insights, I’ll equip you with the best practices for creating compelling ads. Earlier, I shared my personal journey, illustrating how SEO expanded my brand’s reach. Now, we’ll fast forward to a time when I founded a new business. The demand for a swift online presence called for a strategy more rapid than SEO. This is where search engine marketing ads came to the rescue. In less than 24 hours, my business secured a top spot in search results pages, significantly impacting my visibility among potential customers searching for our offerings. These ads facilitated direct engagement with my target audience at the precise moment they were in need of our solutions.
I’m genuinely excited to provide you with in-depth knowledge about online paid advertising. Are you ready to embark on this learning journey? Fantastic! Let’s reconvene in the next video to get started.
Understand the benefits of SEM
Video. Duration: 6 minutes
There are two primary avenues to ensure a business’s presence on search engine results pages: organic search listings and paid advertisements. Paid ads are a key component of the online marketing toolkit and fall under the umbrella of search engine marketing, commonly referred to as SEM. In essence, search engine marketing involves boosting a product or service’s visibility on search engine results pages through paid advertising. For you, as a digital marketer or e-commerce analyst, this could entail the responsibility of setting up SEM-based ads or monitoring their performance to enhance existing campaigns.
When using SEM, you’re likely to incur charges only when someone actively clicks on your ad. This payment model, known as pay-per-click advertising (PPC), allows businesses to pay solely when a user engages with their ad by clicking on it. Unlike other models that charge for ad impressions, PPC is favored by many marketers because it aligns incentives between Google and the advertiser. Google has an incentive to display the right ads that are likely to be clicked, providing a mutually beneficial arrangement. This is in stark contrast to non-digital channels, such as print magazines, where advertisers pay upfront with limited insight into readers’ actions. In digital marketing, we have the unique ability to optimize ad campaigns based on user interactions, which empowers us to better serve potential customers.
A crucial question arises once you decide to embark on SEM advertising: Where do these SEM ads appear? Typically, SEM ads surface at the top and bottom of Google search results, with the exact placement depending on the type of ad. For instance, shopping ads may appear at the top of search results when a user queries a product, or across Google’s online properties, including the shopping tab. Local search ads are another type that appears when a user seeks local businesses, products, or services.
So, why would you opt for SEM as part of your digital marketing strategy? The answer lies in the numerous advantages it offers.
Firstly, SEM enables you to target customers who are genuinely interested in your products or services, increasing the likelihood of conversion. For instance, if you run a plumbing business in Phoenix, Arizona, SEM ensures that your ad surfaces when someone searches for a plumber in that specific region, attracting potential customers with a genuine interest in your services.
Secondly, SEM facilitates quick visibility in search results, proving indispensable for new websites or those seeking visibility for competitive search terms. The immediate impact can bridge the gap as your website builds authority over time.
Another compelling advantage of SEM is the insight it provides into which ads are driving sales. This is particularly beneficial for new websites that lack substantial traffic or comprehensive analytics data. SEM drives targeted traffic to specific pages on your website, enabling you to gauge user interactions, identify high-performing content, and refine areas for improvement.
Finally, SEM bestows you with control over the destination for users clicking on your ads. Unlike ranking high in search listings, which doesn’t guarantee the best page for conversion, SEM offers the flexibility to direct users to precise landing pages optimized for specific keywords or search intents.
To sum it up, SEM is a vital tool that you, as a digital marketer or e-commerce analyst, might utilize to bolster a brand’s online presence. While SEM can be a complex skill to acquire, our course will provide you with a solid foundation and working knowledge of SEM and Google Ads by its conclusion.
Common SEM terms
Reading. Duration: 10 minutes
The purpose of this reading is to introduce basic terms related to search engine marketing (SEM) in Google Ads. Learning these terms will make it easier to understand future SEM content in this course.
Common Advertising Terms
-
Digital advertising: communication made by a company to promote its brand, product, or service using various platforms and online channels.
-
Traditional advertising: non-digital placements, like newspapers, radio, TV, or billboards.
Common SEM Terms
-
Clicks: an interaction with an ad and online user. Clicks can help you understand how well your ad is appealing to people who see it.
-
Impressions: how often your ad is shown. An impression is counted each time your ad is shown on a search result page or other site in the Google Network.
-
Organic results: search results not paid for by advertisers.
-
Paid results: search results that advertisers pay to show whenever a user runs a search containing certain words or phrases (known as ‘keywords’).
-
SERPs: search engine results pages, which are Google’s response to a user’s search query.
-
Visitors: the total number of times people have been to your website or app as a result of clicking your ad.
Digital Advertising Terms
-
Landing page: the webpage where people end up after they click your ad.
-
Optimization score: an estimate of how well your Google Ads account is set to perform. Optimization score runs from 0% to 100%, with 100% meaning that your account can perform at its full potential.
-
Targeted location: the towns, cities, or countries where your ads will appear.
For a list of all the terms presented in Course 2, check out the term glossary at the end of the course.
Common SEM ad formats in Google Ads
Video. Duration: 4 minutes
You might be curious about what these ad formats in Google Ads look like and when they are most effectively used. In this segment, we’ll explore various types of Google Ads. Over time, the ads appearing in Google Search results have undergone changes to align with the primary objective of meeting searchers’ needs. As a digital marketer, you’ll utilize these ads to cater to the requirements of your potential customers. Let’s delve into the diverse ad types you’ll encounter in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Text ads are the quintessential ads featuring a clickable title that leads to a webpage. Following the title is a concise description intended to entice the searcher and provide a glimpse of what awaits them upon clicking.
Shopping ads cater specifically to e-commerce enterprises, showcasing products relevant to the search query. Often, products from various companies are displayed through shopping ads. This ad type differs from text ads in that it includes an image of the product directly in the SERPs.
Local services ads are tailored for businesses serving local customers with various services, such as locksmiths, plumbers, electricians, and real estate agents. To run a local services ad, a business must undergo Google’s screening process, a verification of its legitimacy, which adds to its credibility with potential customers.
Google Maps ads are also designed for local businesses but can include local product-based businesses. Examples include restaurants, jewelry stores, and fitness gyms. These ads help customers find the business’s location and access it on Google Maps.
Call ads are exclusively for mobile searches, as they have gained popularity with the increasing use of mobile devices for search. Call ads enable potential customers to initiate a phone call to the business by simply clicking the ad.
For many Google ad types, there are additional options called ad extensions. Ad extensions provide extra information about a business, such as supplementary website links, contact numbers, or addresses. Several ad extensions are available, with a few key ones worth noting:
- Sitelink extensions offer additional website links that can be useful to searchers.
- Call extensions facilitate direct calls to a business by clicking on the ad.
- Location extensions help customers locate a local business on Google Maps.
- Price extensions, primarily for e-commerce, list specific products and their prices, linking directly to the product page.
- Structured snippets extensions highlight specific aspects of products and services, utilizing categories like services, brands, amenities, types, and styles.
In addition to traditional search engine platforms, some digital marketers also consider YouTube a search engine in its own right. Your potential customers may rely on YouTube to find solutions to their problems, making it a viable advertising platform. A notable advantage of YouTube is the ability to reach potential customers while they’re in the process of researching a product or service, often during the consideration phase of the marketing funnel. For example, a car dealership can advertise to potential customers while they’re watching car reviews.
Search engine marketing is an ever-evolving realm of advertising, with Google constantly improving its ability to serve searchers. Consequently, various ad types and extensions continue to evolve. As a marketer or e-commerce analyst, it’s crucial to remain informed about the available online advertising opportunities.
Google Ads bid strategies
Reading. Duration: 20 minutes
Every Google Ads campaign requires a bid strategy, and determining the correct strategy is key for the success of a business campaign with Google Ads.
This reading will discuss bid strategies and the different types you can choose from.
What is a bid strategy?
A bid strategy is designed to help achieve campaign goals based on budget.
The most basic bid strategy is Manual Cost Per Click (CPC). With manual CPC bidding, you set your own maximum cost per click for your ads.
Alternatively, automated bidding strategies allow Google Ads to automatically set bids for your ads based on an ad’s likelihood to result in a click or conversion that helps you achieve a specific goal.
What is Smart Bidding?
Smart bidding is a subset of automated bidding strategies. These strategies use machine learning to optimize for conversions or conversion value with each auction, and they factor in a wide range of auction-time signals such as the user’s device, location, time of day, remarketing list, language, and operating system. This means that based on these factors and the context of every search, the bid strategy automatically determines whether or not to bid, and how much to bid.
Types of bid strategies

Selecting a bid strategy
While creating a campaign, Google Ads guides you to choose a bid strategy by asking a series of questions to determine your campaign goals. This is useful if you are unfamiliar with specific bidding strategies.
However, the website offers the option to select a bid strategy directly. Once selected, users can choose specific bidding strategies from a drop-down menu.


Key Takeaways
With so many to choose from, bid strategies can sometimes be confusing to navigate. To make your decision easier, be sure to identify what your goal is first and then match it to the appropriate strategy. Choosing the right strategy often takes trial and error, so don’t worry if your selected strategy doesn’t work initially. You can always apply what you’ve learned from previous attempts to your next campaign.
Resources for more information
Choosing the right bid strategy is important for the success of your campaign. For more information on bidding strategies, check out the resources below.
Ginny - SEM and how to attract customers
Video. Duration: 3 minutes
Hello, I’m Ginny, and my role at Google is as an Ads Product Liaison. As the Ads Product Liaison, my primary responsibility is to serve as a bridge connecting our advertiser community, whether they’re working within agencies, in-house as practitioners, or acting as SEM consultants. I aim to address their queries, understand their concerns, and help resolve issues they might encounter with various SEM products and strategies. I act as a vital link between the external SEM professionals and internal teams dedicated to developing SEM products, communications, and marketing strategies.
Throughout my career, I’ve had the opportunity to work on various SEM platforms, including Google Ads, Microsoft Advertising, and several social media channels such as Facebook, Pinterest, Instagram, and Snapchat, as well as Amazon Advertising. Each platform has its unique characteristics, and there’s always a learning curve associated with them. However, the core principles remain constant: it’s about reaching the intended audience effectively with creative content that resonates with them.
I’d like to share a notable success story that underlines the importance of audience-centric strategies. We were tasked with running a campaign for a summer high school program at a university. To succeed, we had to consider both high school students looking for summer activities and their parents seeking suitable programs for their children. This required tailoring our approaches to both audiences, including budget allocation. Since parents were likely to make the financial commitment, we directed a significant portion of the budget towards this audience. It wasn’t just about messaging; it was about strategically distributing the budget where it mattered most. This approach, targeting both students and parents while heavily prioritizing parents, significantly boosted conversions, leads in this case, and made the campaign a resounding success for the university.
One of the most exciting aspects of SEM is its dynamic nature. It’s constantly evolving, and this ever-changing landscape is what keeps it engaging and challenging. Strategies must adapt, and automation is playing an increasingly significant role in SEM. What makes SEM particularly rewarding is the instant gratification it offers. You can witness the impact of your efforts in real time, whether it’s in the form of leads, sales, downloads, or any desired action from your prospective customers. This ability to see the direct influence on business outcomes is incredibly satisfying and fulfilling.
For those who aspire to excel in SEM, one crucial trait to possess is curiosity. You must be naturally inquisitive, eager to learn, and open to embracing the unexpected. Every day presents new opportunities to explore and innovate in this ever-evolving field.
Test your knowledge: Understand search engine marketing (SEM)
Practice Quiz. 4 questions. Grade: 100%
2. Understand Google Ads
How Google Ads works
Video. Duration: 6 minutes
As we’ve previously discussed, Google offers various ad formats, ranging from search ads to shopping and video ads. Regardless of the ad format, you’ll likely follow a set of fundamental steps when creating any Google ad. These critical steps will be explained in this video.
Steps to create a Google As
-
Your initial step is to define your campaign goal. This involves deciding what you aim to achieve with your ad. Do you want to increase sales, generate more leads, boost website traffic, or encourage in-store visits? Your chosen goal shapes the rest of your campaign options. For instance, if your objective is to drive more website traffic, you may opt for a bidding strategy like “maximize clicks” to direct your ad spend towards generating clicks. You might also encounter the term “objective,” which is essentially synonymous with “goal” in the context of Google Ads.
-
Your second step is to select the appropriate campaign type for your ad. Campaigns are used to group ads that share a common budget, location targeting, and other settings. Your Google Ads account can house multiple campaigns simultaneously, each designed for a specific product or service category.
-
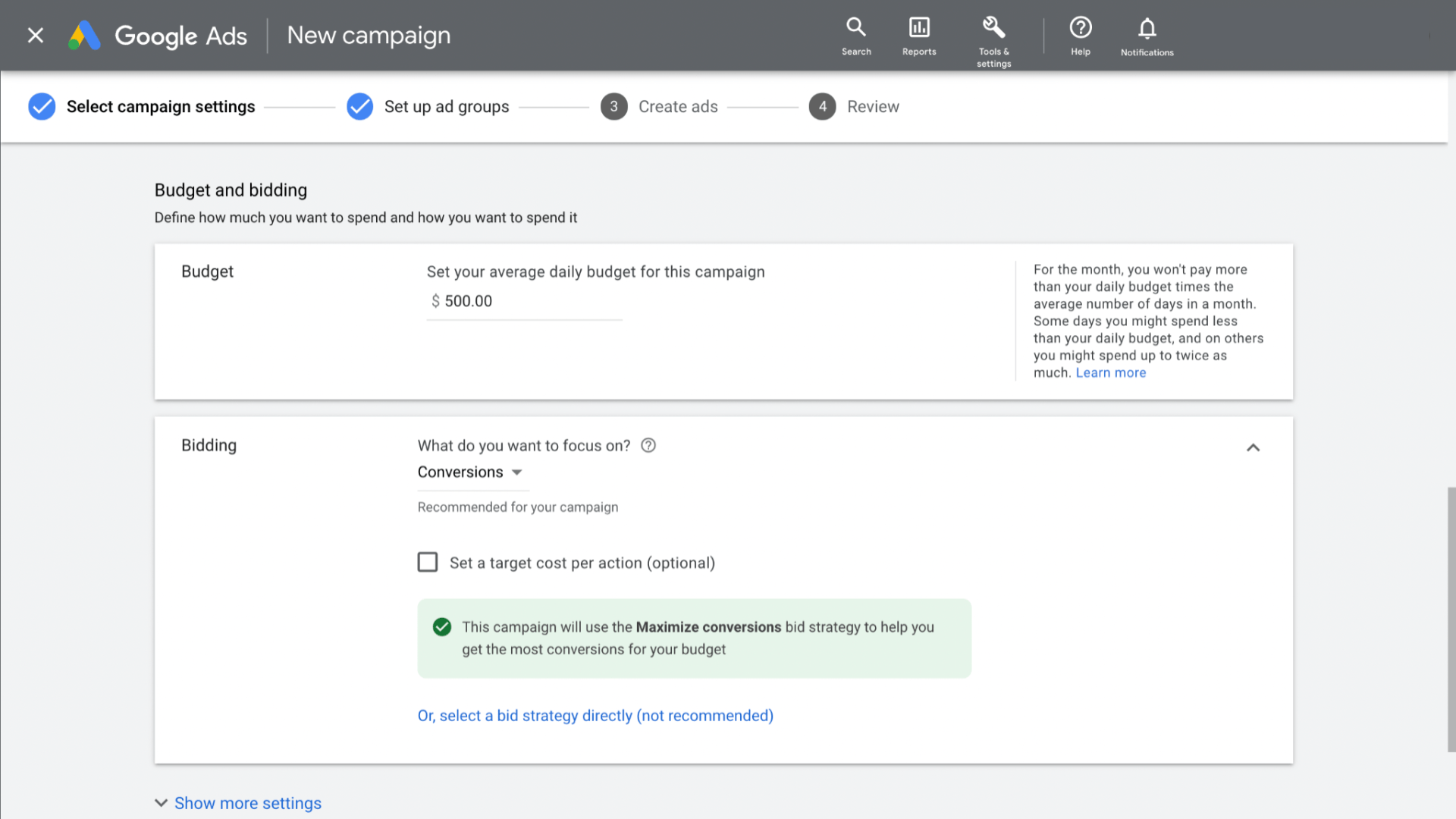
The third step involves setting a budget for your campaign. This budget indicates the maximum amount you’re willing to spend, and you can adjust it at any time. You’ll establish a daily average budget, specifying how much you intend to spend each day within a month. Google Ads optimizes your campaign spend, distributing it based on your bid strategy and factors like daily search traffic variations. While some days may not reach your daily budget, others may exceed it, but you will never surpass your monthly spending limit.
-
The fourth step is to choose your bidding strategy. If you’ve specified a campaign goal, Google Ads will recommend a suitable bidding strategy. You can also select your own bidding strategy to align with your campaign’s specific objective. This may include focusing on conversions or employing an automated bidding strategy. Automated strategies often harness machine learning to enhance ad performance, using software instructions to guide the ad towards its goal.
-
In the fifth step, you’ll determine your audience targeting. Audience targeting narrows down your ad’s reach to specific groups interested in your offerings. This is where customer personas come into play, helping you tailor your targeting for the best results. Common forms of targeting include keywords, audience segments, locations, topics, and device preferences. Planning your targeting in advance can prevent mistakes during the ad creation process.
-
The sixth step involves creating your ad. Responsive search ads, with multiple headlines, descriptions, and a landing page URL, are a primary text ad format. Google Ads automatically tests various combinations to identify the most effective ones. Remember, a well-crafted ad is just part of the conversion process; your landing page must meet the user’s expectations to retain potential customers.
-
The seventh step is setting up conversions. Tracking conversions helps gauge the success of your ads and campaigns. Conversion tracking often involves tools like Google Analytics, which links directly to your Google Ads account. You’ll need to provide clear information to users about the data you collect and seek their consent, usually through a pop-up and an agreement button. Consent and data collection practices are vital considerations in conversion tracking.
While it may initially seem overwhelming, creating a Google ad involves a series of structured steps. With experience and understanding of the platform, this process will become more manageable and familiar over time. Stick with it, and you’ll become proficient in no time.
Case study: How Studley’s Flower Gardens uses Google Ads to grow their business
Reading. Duration: 20 minutes
Search engine marketing and Google Ads help companies get their products and services in front of their ideal customers. Potential customers use Google and other search engines to search for a product or brand. For example, Google Ads Search campaigns help get the business in front of that person right when they’re searching for a solution.
In this case study, explore how the Rochester, New Hampshire-based company Studley’s Flower Gardens uses Google Ads to get their flower and plant products in front of their ideal local customers online.

Company background
Founded in 1928, Studley’s Flower Gardens is a family-owned florist, garden center, and landscaping company located in downtown Rochester, New Hampshire.
In addition to a physical storefront, Studley’s also has a robust e-commerce website. The website’s wide, visually appealing assortment of flowers and plants helps customers find and purchase products online.
Online advertising makes up the majority of its marketing budget. Around 65% of its yearly advertising budget is spent on online ads, and 35% on local radio and television ads.
The challenge
Because Studley’s is a local small business, a challenge it faces is competing with national flower brands in Google’s search engine results pages. Search engine optimization (SEO) can particularly be difficult. National flower brands have large budgets and several team members dedicated to optimizing content to rank higher in search results.
As a small business, Studley’s doesn’t have the team or budget to consistently compete well in the search results. While it does have high search rankings for several local-based keywords, the rankings can fluctuate depending on the search terms. Studley’s cannot rely on consistent high rankings for the flower and plant-based keywords their potential customers are searching for. A change in the search results page rankings can affect its revenue.
The approach
To ensure a consistent presence in Google’s search results for related keywords, Studley’s Flower Gardens uses Google Ads. Instead of using a broad marketing approach, such as a direct mail campaign, Google Ads allows Studley’s to get its ads in front of very specific customers searching for its products or brand name near the business.
For example, Studley’s bids for keywords related to its business’s name. When someone in Rochester, New Hampshire searches for its business name, Studley’s wants to appear right at the top so its potential customers can find its website quickly and easily.
Additionally, instead of trying to manage the Google Ads themselves, the family-owned business hired a marketing company to assist with the ads. Professional digital marketers and Google Ads managers make the decisions on what ads strategies are working well and which need to be improved or removed.
With this approach, Studley’s owners don’t have to spend their time keeping up-to-date with the latest Google Ads software or product changes. Studley’s owners can focus on what they do best—operating and growing their flower and garden center business.
The results
By using Google Ads, Studley’s Flower Gardens gets advertisements in front of potential customers right when they need flowers and plants.
For instance, when a customer searches for Studley’s brand name, the potential customer will likely encounter the ad in the search engine results page, in addition to the website in the search listings. When a potential customer searches for flower delivery near the business, the customer will likely see the ad, even if the website doesn’t appear in the search listings from search engine optimization.
Conclusion
Search engine marketing and Google Ads can help both smaller, local businesses and larger, national-based businesses. The local targeting, such as in Rochester, New Hampshire, allows Studley’s to serve ads to its ideal local customers. Google Ads allow smaller businesses that may not be able to compete with search engine optimization to compete against the larger brands.
As a future digital marketer, realize that you may have an opportunity to help a small business like Studley’s. If you work for a marketing company, you may have dozens of clients that you manage ads for. It’s rewarding to know that the work you do with search engine marketing helps small businesses, just like Studley’s, serve its local communities well.
Identify keywords and understand the ad auction
Video. Duration: 5 minutes
When it comes to search engine marketing, keywords play a foundational role. Targeting the right potential customers is essential to ensure you’re not missing out on valuable traffic. Accurate keyword research is the starting point, as keywords are essentially the words or phrases potential customers enter into Google Search.
When selecting keywords for Google Ads, you don’t necessarily have to input each keyword precisely. Instead, you can utilize keyword match types, which specify the level of similarity required between the keyword and the user’s query for the ad to be displayed. There are three primary keyword match types: broad match, phrase match, and exact match.
-
Broad match allows your ads to appear on phrases related to your keyword, which may not include the keyword itself. For instance, “low-carb diet plan” might also trigger ads for searches like “carb-free foods” or “low-calorie recipes.” Broad match considers the user’s recent search history and the content of the landing page to ensure relevant matches. Notably, the landing page plays a pivotal role in Google Ads success.
-
Phrase match involves keywords that encompass the meaning of your chosen keyword. It offers greater flexibility than exact match but is more targeted than broad match. For example, if your keyword is “tennis shoes,” your ad may appear for searches like “shoes for tennis” or “buy tennis shoes on sale,” but not for unrelated queries such as “tennis rackets.”
-
Exact match, on the other hand, displays ads for searches with the same intent as the keyword. It offers the highest level of control over ad targeting. For instance, if your keyword is “shoes for men,” your ad may appear for searches like “shoes men” or “men shoes,” but not for unrelated queries like “men’s tennis shoes.”
All three match types can account for variations such as plurals, synonyms, misspellings, and reordering of words. This means you typically don’t need exhaustive keyword lists that encompass all these variations.
While determining keywords for your Google Ads, it’s important to consider negative keywords. Negative keywords exclude specific search terms from your ad campaigns, preventing irrelevant searches. Google Ads emphasize the importance of keyword-content alignment and its impact on the ad auction.
The ad auction is how Google decides which ads to display and their order for search results with text ads. The position of your ads on a given search result is referred to as ad rank, a value Google uses to determine an ad’s position. Ad rank is determined by three key factors.
Factors that determine ad rank
-
Firstly, there’s your bid, representing the amount you’re willing to pay each time a potential customer clicks on your ad. A higher bid can result in a higher ad position within the SERPs.
-
Secondly, the quality of your ads and landing page is assessed. Google evaluates the relevance of your ads and landing page to the user’s query, as well as the likelihood of a user clicking your ad. Quality score, not used in the auction itself but helpful for ad effectiveness, is presented on a scale of 1-10.
-
Lastly, ad extensions, which provide additional information like a phone number or extra links to your website, also factor into ad rank. It’s advisable to utilize all relevant ad extensions for your business.
These three factors collectively influence when and if your ad appears to potential customers. It’s worth noting that other ad rank factors, such as search content and other page results, also play a role. Hence, aligning your ad with the right keywords is crucial, as mismatched keywords may lead to your ads being displayed to the wrong audience, impacting your ad rank.
With keywords closely aligned, the right bid, a quality ad, and a user-friendly landing page, you significantly increase your chances of having your ad prominently featured in Google search results.
Best practices when creating a Google Ad in Search
Video. Duration: 4 minutes
Creating an effective search ad is essential for improving your online presence and driving better results. Here, we’ll delve into best practices for crafting Google Ads for Search. Why should you care about creating an effective ad? Well, a well-executed ad can lead to higher visibility in search results, more clicks, increased conversions, and even a lower cost per click compared to your competitors. To optimize your Google Ads for Search, consider the following best practices:
-
Focus on User Needs and Benefits:
- Tailor your ad messaging to address user needs and emphasize the benefits your product or service offers.
- By aligning your ad with what matters most to potential customers, you increase the likelihood of engagement.
- Think about what users want from your ad—whether it’s reliability, variety, or trustworthiness— and incorporate language that resonates with their interests.
- Utilize customer personas to understand their goals and integrate them into your ad copy.
-
Incorporate Keywords in Headlines:
- Include at least one relevant keyword from your ad group in your ad headlines.
- Keep in mind that the headline is the clickable link at the top of your ad, making it a crucial element.
- Since Google automatically tests combinations of headlines and descriptions, ensure that any combination reads smoothly.
- Incorporating keywords is vital as it aligns your ad with what potential customers are actively searching for.
-
Avoid Generic Sales Language:
- Steer clear of generic sales phrases like “call us today” that create a false sense of urgency.
- Prioritize user benefits in your calls to action, ensuring that the customer perceives value in taking immediate action.
- Instead of generic, non-specific calls to action like “sign up today” or “book today,” opt for specific and relatable alternatives.
- Tailor your calls to action to meet the specific desires of potential customers.
-
Leverage Ad Extensions:
- Implement all relevant ad extensions that provide additional information about your business.
- Ad extensions enhance the appeal of your ads by offering valuable details to potential customers.
- Using ad extensions can make your ads more prominent in search results and improve the overall user experience, especially for mobile users.
- Aim to enable multiple ad extensions, ideally at least four, as Google Ads selects the best combination for each auction.
-
Optimize Your Landing Page:
- Understand that your ad and landing page work in tandem to deliver a seamless user experience.
- Ensure your landing page aligns with the user’s search intent by comparing your keywords to the page’s content.
- While the exact keywords don’t need to be on the landing page, the relevancy should be evident.
- Evaluate the usefulness, organization, and clarity of your landing page to ensure it meets user expectations.
- Speed up page loading times to prevent user frustration, which may adversely affect your ad’s performance.
As you apply these best practices, think of creating Google Ads as an ongoing experiment. Continuously monitor performance, collect feedback, and make necessary adjustments to enhance your ads and landing pages. The goal is to consistently deliver the best ad experiences to your potential customers. Nice work!
Google Ads account structure and organization explanation
Reading. Duration: 10 minutes
In a video, you learned about Google Ads, campaigns, and Ad Groups. This reading will help you learn how these items are organized within Google Ads.
Google Ads is Google’s online advertising program. Through Google Ads, you can create online ads to reach people exactly when they’re interested in the products and services that you offer.

Google Ads account structure

The following items are presented in the order that you will experience them while creating a campaign in Google Ads. Refer to the definitions as you follow the diagram above.
-
Google Ads: Google’s online advertising program. Through Google Ads, you can create online ads to reach people exactly when they’re interested in the products and services that you offer.
-
Campaign: A plan of action for how a set of one or more ad groups that share a budget, location targeting, and other settings will be distributed online. Campaigns are often used to organize categories of products or services that you offer.
-
Average daily budget: The average amount that you set for each ad campaign on a per-day basis. It specifies roughly how much you are comfortable spending each day over the course of the month.
-
Ad Groups: The way to organize and target ads into themed groups of keywords. Each of your campaigns is made up of one or more ad groups.
-
Ad Formats: Text, videos, images, digital content ads, and more that appear alongside used to promote products and services with Google Ads.
-
Bids: The amount you’re willing to spend each time a potential customer clicks your ad or calls you is known as a bid.
-
Keywords: These are words or phrases describing your product or service that you choose to help determine when and where your ad can appear. Advertisers bid against each other, and ads are ranked based on how high you bid and how relevant your ad is, among other factors.
Creating a Google Ad
Reading. Duration: 20 minutes
Previously, you learned about Google Ads and the different types of Google Ad formats. This reading will provide an overview of the seven steps to creating a responsive search ad based on your stated objective.
These instructions are based on the Google Ad interface, which offers guidance along the way.
You can opt to create a campaign without defining a goal for guidance by selecting the option when presented on screen.
Seven steps to create a Google Ad campaign
-
Define your campaign goal
Your goal is what you want to achieve with the ad. There are seven campaign objectives to choose from:
- Sales: drives sales online, in app, by phone, or in-store.
- Leads: brings in leads and other conversions by encouraging customers to take action.
- Website traffic: encourages people to visit your website.
- Product and brand consideration: encourages people to explore your products or services.
- Brand awareness and reach: reaches a broad audience and builds awareness.
- App promotion: increases installs or promotions for your mobile app.
- Local store visits and promotions: encourages customers to visit a physical store location.

-
Choose the campaign type
Next, choose your campaign type. Options include:
- Search
- Performance Max
- Display
- Shopping
- Video
- Discovery


-
Set a budget
Once you select your campaign, move on to set your budget. For more information on setting your budget, visit the Google Ads Help Center.

-
Choose your bidding strategy
Refer to a previous reading on bidding strategies to review the different types.
-
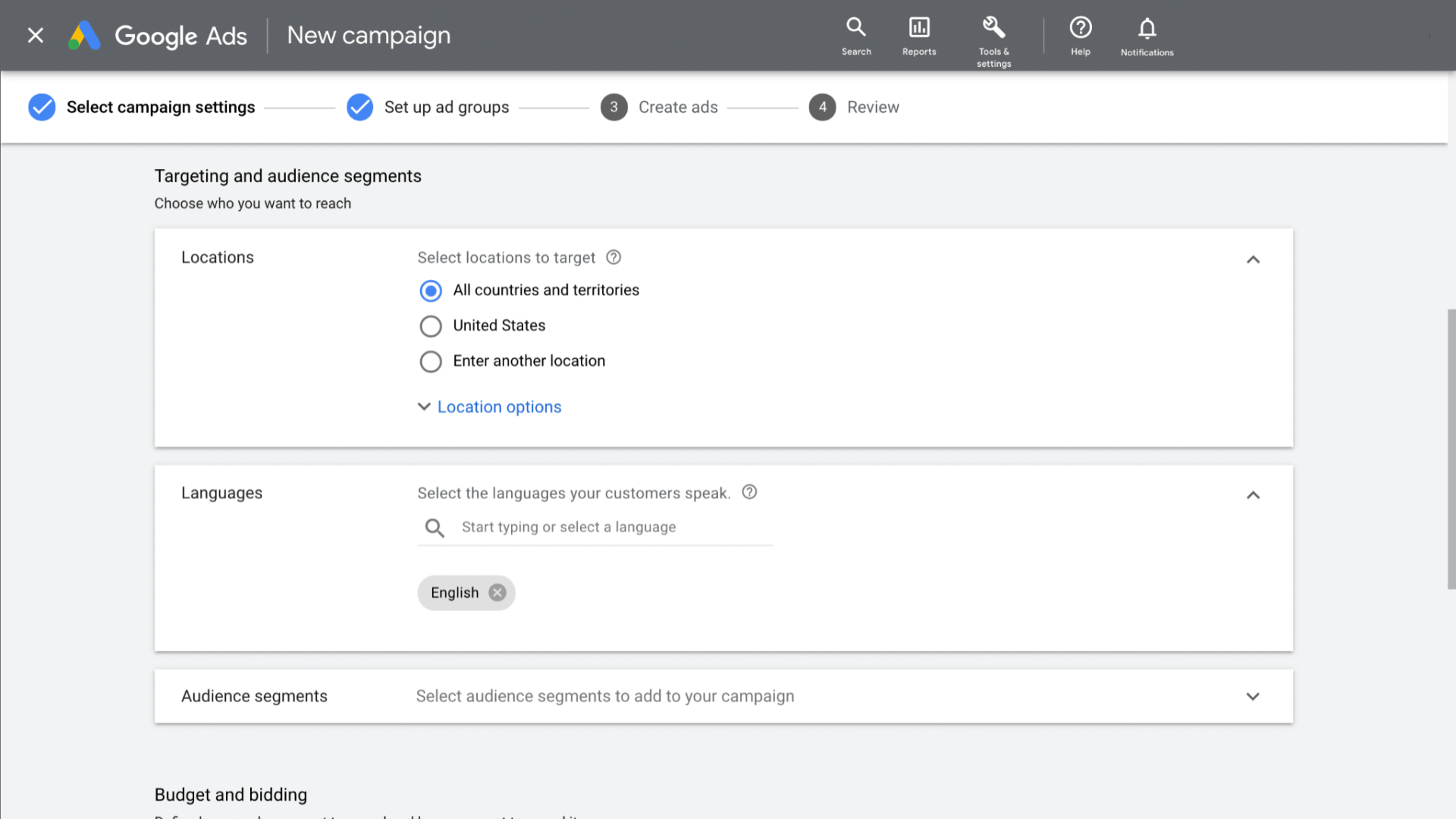
Select your targeting
Targeting helps define how narrow or broad your audience targeting will be. Your target categories include:
-
Locations
-
Languages
-
Audience segments
-
-
Create your ad
To create your ad, input information to determine how your ad will appear online. This includes:
- Descriptions
- Final URL
- Display path
- Headlines
- Extensions
Be sure to include at least one of your keywords in your headlines and create headlines that are relevant to the keywords you’re targeting. Also, use the ad strength indicator as a guide to improving the effectiveness of your ads. Ad strength provides you with feedback to help you focus on providing the right messages to your customers.

-
Finalize your ad
Once you are ready, finalize your ad by adding your final URL and display path. Use the preview window on the screen to check how your ad will appear online.

Resources for more information
For more information on creating a Google Ads campaign, visit the following resources:
- Create effective Search ads: This Google Help center article provides information for optimizing ads and messaging on Google Search.
Activity: Create an effective responsive search ad
Practice Quiz. 1 question. Grade: 100%
Activity Overview
In this activity, you will practice writing headlines, descriptions, and ad extensions for a Google responsive search ad. Responsive search ads allow you to create ads that are customized to your customers’ searches, improving your campaign’s performance. To complete this activity, you’ll craft multiple headlines, descriptions, and ad extensions relevant to your keywords.
Scenario
Review the scenario below. Then complete the step-by-step instructions.
Oscar’s Bakery specializes in vegan, organic, and gluten-free baked goods. They have just launched a website feature that allows customers to order online. To promote this new feature, they are offering free delivery and 15% off on all online orders.
You are working on a responsive search ad for your ad group. Before entering the relevant details into the Google Ads tool, you will organize it in a spreadsheet. In order to improve your ad’s performance, you will craft multiple headlines and descriptions that are relevant to your keywords to try to match your potential customers’ search queries. You will also write ad extensions to provide additional important information.
You can use the information listed below about Oscar’s Bakery to help you craft headlines, descriptions, and ad extensions. You may also supply details of your own.
Your goal is to create compelling ad content.
Oscar’s Bakery information:
-
Based in Boulder, Colorado
-
Founded in 1987
-
Offers healthy vegan, organic, and gluten-free baked goods
-
Open seven days a week
-
Uses local ingredients
-
Offers 25 different flavors of cupcakes
-
Provides the widest variety of baked goods in Boulder
-
Bakes custom cakes
-
Has won multiple awards
Step-By-Step Instructions
Step 1: Access the Template
To start, access the Responsive search ad organizer template.
Step 2: Write headlines
The headline is the clickable link at the top of the ad, and it is the ad’s most prominent text. The content and quality of your headlines will impact how well your ad performs.
To begin, add 10 headlines for your ad to the Headlines column in the organizer template. Headlines have a 30-character limit. (The cell next to each headline will automatically calculate the number of characters in the headline.) Follow these best practices when writing your headlines:
-
Craft your messaging to focus on the needs and benefits of your user. Oscar’s Bakery customers will likely have an interest in organic, vegan, and/or gluten-free baked goods.
-
Write at least two headlines that include relevant keywords from the Keywords column. Keywords help connect your ad with what customers are searching for, making them more likely to click on it.
-
Write at least three headlines that do not include keywords. Instead, highlight the benefits and features of your business, a problem you’re solving, or delivery information.
-
Write headlines of different lengths. Longer headlines increase the clickable space of your search ads, but shorter headlines may perform better with people already searching for your brand.
-
Use specific and relevant calls-to-action. So instead of a generic call-to-action like “Order Online,” you might include one that’s tailored to your brand like “Order Online for Free Delivery.”
-
Make each of your headlines unique. Don’t use the same or similar phrases in any of your headlines.
Step 3: Write descriptions
Descriptions appear below the headline in your search ad. Descriptions are longer than headlines, so they give you the chance to really highlight what makes the business special.
Now, add five descriptions for your ad to the Descriptions column in the template. Descriptions have a 90-character limit. (The cell next to each description will automatically calculate the number of characters in the description.)
In addition to applying the best practices described for writing headlines above—such as focusing on user benefits, including relevant keywords, and adding specific calls-to-action—your descriptions should highlight additional information about your business that isn’t mentioned in your headlines. Headlines and descriptions can show in multiple combinations and in any order, so be sure that any combination is clear and understandable.
Step 4: Write callout extensions
Ad extensions make your search ads more appealing by allowing you to show users additional helpful information, such as your phone number or location, or a link to a specific page on your website. They also make your ads more prominent on the results page.
There are a number of different types of ad extensions. Callout extensions promote unique offers, like free shipping or 24-hour customer service, and important details about your business.
Finally, add five callout extensions for your ad to the “Ad Extensions” column in the template. Callout extensions have a 25-character limit. (The cell next to each extension will automatically calculate the number of characters in the extension.)
Follow these best practices when writing your extensions:
-
Keep text short. Callout extensions should focus on individual aspects of your business in a few words or a short phrase. For example, you might say “Free Delivery” instead of “We offer free delivery.”
-
Be specific. Provide details to customers to help them decide if you have what they’re looking for. “Award-Winning Baked Goods” is a more effective callout than just “Baked Goods,” for instance.
-
Ensure that the content of your extensions is different from the content of your headlines and descriptions.
Pro Tip: Save your work
Finally, be sure to save the work you did to complete this activity. This can help you work through your thought processes and demonstrate your experience to potential employers
What to Include in Your Response
Be sure to include the following elements in your completed spreadsheet:
-
10 headlines
-
5 descriptions
-
5 callout extensions
Activity Exemplar: Create an effective responsive search ad
Reading. Duration: 10 minutes
Here is a completed exemplar along with an explanation of how the exemplar fulfills the expectations for the activity.
Completed Exemplar
To review the exemplar for this course item, click the link below and select “Use Template.”
Link to exemplar: Responsive search ad organizer
Assessment of Exemplar
Compare the exemplar to your completed spreadsheet. Review your work using each of the criteria in the exemplar. What did you do well? Where can you improve? Use your answers to these questions to guide you as you continue to progress through the course.
Your responsive search ad organizer should include:
-
10 headlines of different lengths that are unique, focus on the needs of the user, include keywords, and use relevant calls-to-action.
-
5 descriptions that highlight additional information about your business that isn’t mentioned in your headlines.
-
5 callout extensions that are short, specific, and different from the content in your headlines and descriptions.
Test your knowledge: Apply search engine marketing
Practice Quiz. 4 questions. Grade: 100%
3. Apply display advertising
Introduction to display advertising
Video. Duration: 4 minutes
Exploring Display Advertising
In our previous discussions, we delved into SEM and the art of placing ads on Google Search. Now, let’s explore another avenue of online advertising – display advertising. This approach involves getting your ads featured on websites or apps that aren’t search engines. It’s like putting your children’s furniture ad on a trendy furniture website.
Defining Display Advertising
Display advertising is the marketing term for visual ad formats placed on websites and applications. If you’re a digital marketer for an e-commerce company, you want to target audiences who share interests with your customers. Rather than manually reaching out to websites for ad placements, you can leverage display advertising networks like the Google Display Network.
Google Display Network
The Google Display Network, with over two million websites, videos, and apps, offers an extensive platform for displaying your ads. This network reaches a staggering 90% of internet users globally. Within this vast network, you can employ targeting options to place your ads contextually, by audience, location, and even retargeting past website visitors.
The Significance of Targeting
Getting your ad in front of the right audience is paramount in display advertising. Unlike search ads, where users are actively seeking products or services, display ads are viewed passively. To drive desired actions like sign-ups or purchases, precision targeting is essential.
Types of Google Display Ads
Google Display Ads come in two primary types: uploaded and responsive.
Uploaded Display Ads
Uploaded ads necessitate creating the ad graphic, adhering to specified requirements, and manually uploading the ad. You can choose from various ad sizes, such as banners, leaderboards, and skyscrapers, ideal for a tailored ad design and with the necessary design resources and time.
Responsive Display Ads
On the other hand, responsive display ads streamline the process. You only need to upload content elements like images, headlines, logos, videos, and descriptions. Google Ads automatically generates ad combinations for websites, apps, YouTube, and Gmail. While you have less control over the ad’s appearance, some prefer this option for its simplicity.
Advantages of Responsive Display Ads
Responsive display ads offer several benefits, making them an attractive choice:
- Optimization by Google Ads Software: Google Ads software optimizes ad combinations, automatically determining the best-performing ads using various content elements.
- Broader Reach: Responsive ads adapt to the ad space available, ensuring your ads reach more customers.
- Video Integration: You can enhance your reach by incorporating videos, with Google Ads automatically testing and selecting the best-performing content.
- Time Efficiency: Responsive ads simplify ad management, allowing you to focus on performance improvement, saving you valuable time.
Compared to search advertising, display advertising is more visually oriented and can be complex. However, responsive display ads streamline the process, making it a valuable tool for digital marketers and e-commerce analysts.
How to optimize a responsive display ad for your goals
Video. Duration: 4 minutes
Mastering Responsive Display Ad Best Practices
In the realm of online advertising, responsive display ads have risen to prominence. By implementing these best practices, you can enhance your reach and drive performance. We’ll begin our journey by examining creative best practices, and then we’ll shift our focus to valuable tips for optimizing images.
Creative Best Practices
-
Leverage the Power of Assets:
- Assets constitute the core content of your ad, including headlines, images, descriptions, logos, and business names. To achieve outstanding results, adhere to Google’s recommendation of five headlines, five images, and five descriptions. Remarkably, utilizing multiple headlines, images, and descriptions can boost conversions by up to 10%.
-
Craft Unique and Compelling Copy:
- Headline Excellence: Your headline should be a showcase of your brand or product’s value, capturing the interest and utility for customers. Make it clear and impactful even without relying on a description.
- Description Dynamics: Complement the headline with an engaging description that articulates the product or service’s value concisely to potential customers.
-
Ensure Cohesive Landing Pages:
- Consistency between the ad and the landing page is pivotal. The messaging on your landing page should seamlessly align with your ad’s message. A mismatch can leave potential customers bewildered, potentially leading to disinterest or disengagement.
-
Freshness is Key:
- Rotate new display ads every few weeks to keep your advertising dynamic. Ad improvement is often an iterative process. By replacing underperforming creative assets with fresh content, you maintain the ad’s effectiveness. This prevents your audience from experiencing “ad fatigue,” where overexposure leads to disinterest and inattention.
Optimizing Images
Images are the heart and soul of responsive display ads. They serve as a visual gateway for customers to understand your business, products, and brand. Here are some essential tips for selecting images:
-
Emphasize Visual Focus:
- Choose images with a compelling visual focal point that aligns with your ad’s core message. Such images tend to deliver the best results.
- Avoid overlaying the image with logos, text, or buttons. Overly repetitive logos and unreadable text in smaller ad formats can hamper performance. Also, steer clear of buttons like “Book Now” or “Download” to ensure compliance with Google’s ad policies.
-
Make the Product Shine:
- If you’re promoting a product, ensure it takes center stage in the image. Keep blank space under 80% to maximize the product’s visibility. This consideration is especially crucial for product photoshoots.
-
Background Harmony:
- Choose backgrounds that naturally complement the product, avoiding artificial or incongruous settings. Images with physical settings, natural lighting, and shadows tend to resonate better with viewers.
Navigating Google Ads’ image policies and recommendations may initially appear complex, but once understood, it becomes a powerful tool for digital marketers and e-commerce analysts. Responsive display ads, introduced by Google in 2016, offer an advanced software-driven approach to creating effective and high-performing ads. If your role calls for it, don’t miss the opportunity to harness this tool to your advantage.
Advertise on YouTube
Reading. Duration: 20 minutes
With millions of videos uploaded daily, the video sharing platform YouTube offers a great opportunity for brands to reach a variety of audiences all over the world.
In this reading, you will learn about advertising on YouTube, including the benefits and the different ad formats offered.
Display ads vs. TrueView video ads
Before you learn about the benefits of advertising on YouTube, it’s important to know that there are two different types of ads on YouTube: Display ads and TrueView Ads. This can sometimes be confusing as they are both often referred to as just “YouTube ads.”
Display ads
As you have learned, Display ads are visual ad formats placed on websites or applications. They are static ads created in Google Ads using Display campaigns. Think of them as digital billboards. Display ads use the Google Display Network, which is a group of websites, videos, and apps where ads can appear. When on YouTube, these ads appear next to the streaming video. Revisit an earlier lesson on Display ads for further information.

TrueView Video Ads
Alternatively, TrueView ads are video advertisements. They are called “trueview” because brands only pay when someone chooses to view them. While these ads are also managed in Google Ads, advertisers must first upload their videos to their YouTube channel before creating a campaign.
After uploading your video ad to your brand’s channel, there are a variety of different ad formats to choose from. These include: skippable video ads, non-skippable video ads, overlay ads, and in-feed ads.
- Skippable video ads allow viewers to skip ads after five seconds.

- Non-skippable video ads must be watched before a video can be viewed. They run between 15 to 20 seconds, depending on regional standards. A subcategory of non-skippable ads is bumper ads.These ads run for just six seconds.

- Overlay image or text ads appear on the lower 20% portion of a video. Unlike the other TrueView ads, overlay ads can only be viewed on computers and not mobile devices.

- In-display ads, also known as TrueView Discovery Ads, appear in the YouTube search results for video queries with related topics. They include a video thumbnail, title, and description. Think of them as Search ads with videos instead of webpage links. When selected, they can be watched in full—independent from other videos.

Benefits of advertising on YouTube
There are a number of reasons why advertising on YouTube is beneficial to most brands. The most recognized reasons are cost, reach, and effectiveness.
YouTube ads are inexpensive
While the production cost of video ads can differ from company to company, it is relatively cheap to run YouTube ads. YouTube ads perform on a pay-per-view, or a pay-per-click model. This means that brands don’t have to pay for an ad until a specific action is taken.
On average, these ads cost between $0.10 to $0.30 (USD) per view or action. The exact cost depends on factors such as watch time, audience targeting, and campaign objective. The low cost is helpful for brands with small budgets or brands with larger budgets seeking to produce many ads.
YouTube ads help you reach your audience
YouTube gives brands the opportunity to reach a variety of audiences who are searching for their brand or topics related to their products. Brands can target customers using specific topics, keywords, or demographics.
Your brand’s video can also appear in the suggested video feed of another video. This means your ads can appear on popular videos that will be seen by a relevant audience.
YouTube ads are effective
With a larger audience, you have more opportunities for viewers to interact with your brand. In fact, people who view an ad are 10 times more likely to engage with the brand behind the ad. This is great for brand awareness and driving sales.
Key takeaways
YouTube is a powerful tool for brand marketers trying to get noticed by relevant audiences. Its capabilities and low cost make it a promising tool to meet your brand needs.
Resources for more information
How to create a responsive display ad
Reading. Duration: 20 minutes
In a previous video, you learned that one type of display ad is a responsive display ad. This reading will explain what responsive display ads are and how to create them.
Create a responsive display ad
Responsive display ads are the default ad type that appear across the Google Display Network, which is a group of more than two million websites, videos, and apps.
Responsive display ads are considered “responsive” because they automatically adjust their size, appearance, and format to fit available ad spaces. Responsive display ads can show any sized text or image. They can even be shown as “native” ads, meaning they can blend into the font and feel of the publisher’s site.
Getting started
Before you upload your assets, you’ll need to complete, gather, or establish the following items related to your brand:
-
Business name: This is the official name of your business or brand. Ensure your company name is spelled and capitalized correctly, as your ad will contain exactly what you provide.
-
Display URL: This is the page the ad will direct customers to once selected. Google’s policy is that your landing page and final URL must share the same domain as your display URL.
-
Display campaign: Before running a responsive display ad, you need to create a display campaign in Google Ads. You learned previously that your campaign is the base of your ads. Here, you will set your budget, bid strategy, ad groups, target audience, etc.
To get started:
-
Log into your Google Ads account.
-
Select the display campaign you want to create ads for.
-
Select Ads & extensions.
-
Select Ads.
-
Select Responsive display ad.
Upload assets
Responsive display ads are an asset-based ad type, which means that you can create them by uploading various assets. When setting up a new responsive display ad in Google Ads, you can upload the following assets when prompted:
Images: These will appear as the primary element of your ad. Your images should:
-
Be high quality and have a strong visual focus
-
Make the product or service the focus of the image
-
Support the main point of the ad
-
Have a background that suits the product
-
Not overlay a logo, text, or buttons
-
Not be blurry, skewed, or use excessive filters
You can upload between 5 to 15 images from your computer, or use a free library of stock images provided by Google. You can also scan your website for relevant images to choose from using a Google Ads feature.
Logos: Your brand’s official logo will also appear in the ad. It should be a 1:1 ratio image, or square. The recommended size is 1200 x 1200 px.
Short Headlines: You’ll be asked to write at least five short headlines. These are the first lines of your ads and will appear in tight ad spaces where long headlines don’t fit. Short headlines may appear with or without your description and are 30 characters or fewer.
Long Headlines: You’ll be prompted to write one long headline. These will appear in larger or longer ads and are 90 characters or fewer. Both short and long headlines should:
-
Be written in sentence case (i.e., only capitalize the first letter of the first word, except for proper nouns)
-
Incorporate unique and compelling copy that demonstrates your brand or product’s value
-
Stand alone without the support of a description
-
Describe any promotions or special offers
-
Tell customers what to do
Descriptions: You’ll need to write up to five distinct descriptions about your product or service that encourages your audience to act. Each description has a 90 character limit. Your descriptions should:
-
Be written in sentence case
-
Complement your headlines
-
Explain your product or service’s value clearly
-
Include unique selling points, prices, and promotions
-
Explain in more detail why customers should trust your brand
-
List ratings and reviews
Videos: Videos are an optional asset. If you choose to include videos, they must be a length of 30 seconds or fewer, and the video must be uploaded to YouTube before creating your ad.
Once you enter your assets and publish your ad, Google Ads will automatically generate the best ad combinations for available spaces based on what you upload, so upload as many assets as you can, if applicable. The more assets you have, the more opportunities Google Ads have to fit your ads in different spaces.
Be sure that you keep accessibility in mind when creating your ads. Viewers with low vision may not be able to read your ads without the assistance of a screen reader, which is an assistive technology that reads aloud the description of text and images. For this reason, keep your headlines and descriptions straightforward and descriptive.
Review performance
Over time, Google uses machine learning to determine which combination of assets work best for your marketing needs and begins to only show the most effective versions of the ad.
Approximately two weeks after launching your ad, Google Ads will collect enough data for you to view the best-performing versions.
If certain responsive display ads are not performing well, you can identify if there is a correlation between the ads and the assets used in those ads. Change out the assets that are receiving little to no traffic for ones you think would achieve more success.
Key takeaways
Responsive display ads rely on the assets you choose. Put time into selecting the best quality images and the most thoughtful headlines and descriptions.
Resources for more information
Get a detailed overview of creating responsive ads:
- Create effective responsive display ads: Read more about creating responsive display ads from Google Ads Help.
Activity: Optimize responsive display ads
Practice Quiz. 1 question. Grade: 100%
Activity Overview
In this activity, you will evaluate assets for responsive display ads and suggest how to optimize them based on creative best practices.
Google’s responsive display ads automatically combine assets—such as headlines, descriptions, images, and logos—to deliver the best-performing ads to potential customers.
Be sure to complete this activity before moving on. The next course item will provide you with a completed exemplar to compare to your own work. You will not be able to access the exemplar until you have completed this activity.
Scenario
Review the scenario below. Then complete the step-by-step instructions.
You work for an agency hired to do marketing for Great Grounds, a small, regional chain of coffee shops based in the Northeast United States. Founded in 1976, Great Grounds sells premium, craft coffee that is roasted by hand daily and freshly brewed to order. For the past two years, they have been voted “Best coffee in the Northeast” by The Northeastern Times.
In order to increase sales on weekday afternoons, Great Grounds is offering a “buy one drink, get one free” deal to customers who purchase between the hours of two and four, Monday through Friday. Your agency has recently hired a marketing intern, and you’ve asked them to begin developing a responsive display ad campaign for this promotion. You’ve provided them with a template to fill out, and now you need to review their work. Considering creative best practices for developing effective responsive display ads, you will evaluate their work and offer suggestions for improvement.
Step-By-Step Instructions
Step 1: Access the template
To use the template for this course item, click the link below and select “Use Template.”
Link to template: Responsive display ad organizer
Step 2: Access supporting materials
The following supporting materials will help you complete this activity. Keep them open as you proceed to the next steps.
To use the supporting materials for this course item, click the link below and select “Use Template.”
Link to supporting materials: Display ad images
Step 3: Evaluate the headlines
The headline is the first line of the Display ad. Review the criteria listed below for crafting effective headlines for responsive display ads.
Responsive display ads should include five short headlines and one long headline that:
-
are written in sentence case
-
include no more than 30 characters each for short headlines and 90 characters each for long headlines
-
incorporate unique and compelling copy that demonstrates the brand or product’s value
-
can stand alone without the support of a description
-
describe any promotions or special offers
-
tell customers what to do
With this criteria in mind, evaluate the headlines in the responsive display ad organizer. Add feedback for any of the headlines to the Short Headline Feedback or Long Headline Feedback columns. Note any areas in which the headlines do not meet the criteria listed above, and offer suggestions for improvements.
If there are fewer than the suggested number of headlines, write additional ones in the Short Headlines or Long Headlines columns and change the color of the text so they stand out.
Step 4: Evaluate the descriptions
The description adds to the headline and invites people to take action. Review the criteria listed below for crafting effective descriptions for responsive display ads.
Responsive display ads should include five descriptions that:
-
are written in sentence case (i.e., only capitalize the first letter of the first word, except for proper nouns)
-
have no more than 90 characters each
-
complement the headlines
-
explain the product or service’s value clearly
-
explain in more detail why customers should trust the brand
-
list ratings and reviews
With this criteria in mind, evaluate the ad’s descriptions in the responsive display ad organizer. Add feedback for any of the descriptions to the Description Feedback column. Note any areas in which the descriptions do not meet the criteria listed above, and offer suggestions for improvements.
If there are fewer than the suggested number of descriptions, write additional ones in the Descriptions column and change the color of the text to make them stand out.
Step 5: Evaluate the images
Images are the most important element of your Display ads. They help customers understand your business, products, and brand. Review the tips listed below for choosing images for responsive display ads.
Responsive display ads should include five images that:
-
are high quality and have a strong visual focus
-
make the product or service the focus of the image
-
support the main point of the ad
-
do not overlay a logo, text, or buttons
-
have a background that suits the product
-
are not blurry, skewed, or use excessive filters
With this criteria in mind, evaluate the ad’s images. Open the Display ad images presentation. Refer to the titles and slide numbers of images in the Images column of the responsive display ad organizer, review the corresponding images in the presentation, and add any feedback to the Image Feedback column. Note any areas in which the images do not meet the criteria listed above, and offer suggestions for improvements.
If there are fewer than the suggested number of images, review the images in the Display ad images presentation and suggest additional ones to include. Add the titles and slide numbers of those images to the Images column of the responsive display ad organizer.
Pro Tip: Save your work
Finally, be sure to save the work you did to complete this activity. This can help you work through your thought processes and demonstrate your experience to potential employers.
What to Include in Your Response
Be sure to address the following elements in your completed responsive display ad organizer:
-
Feedback on the short headlines and long headline
-
Additional headlines so that there are five short headlines and one long headline total
-
Feedback on the descriptions
-
Additional descriptions so that there are five descriptions total
-
Feedback on the images
Titles and slide numbers of additional images so that there are five images total
Activity Exemplar: Optimize responsive display ads
Reading. Duration: 10 minutes
Here is a completed exemplar along with an explanation of how the exemplar fulfills the expectations for the activity.
Completed Exemplar
To review the exemplar for this course item, click the link below and select “Use Template.”
Link to exemplar: Responsive display ad organizer
Assessment of Exemplar
Compare the exemplar to your completed responsive display ads organizer. Review your work using each of the criteria in the exemplar. What did you do well? Where can you improve? Use your answers to these questions to guide you as you continue to progress through the course.
Your responsive display ad organizer should include:
-
Feedback on where the short headlines and long headline do not meet creative best practices
-
Headlines should:
-
be written in sentence case
-
include no more than 30 characters each for short headlines and 90 characters each for long headlines
-
demonstrate the brand or product’s value
-
stand alone without the support of a description
-
describe any promotions or special offers
-
tell customers what to do
-
-
-
Two additional short headlines written to the criteria listed above
-
Feedback on where the descriptions do not meet creative best practices
-
Descriptions should:
-
be written in sentence case
-
include no more than 90 characters each
-
complement the headlines
-
explain the product or service’s value clearly
-
explain in more detail why customers should trust the brand
-
list ratings and reviews
-
-
-
One additional description written to the criteria listed above
-
Feedback on where the images do not meet creative best practices
-
Images should:
-
be high quality and have a strong visual focus
-
make the product or service the focus of the image
-
support the main point of the ad
-
not include a logo, text, or button overlay
-
have a background that suits the product
-
not be blurry, skewed, or use excessive filters
-
-
-
The titles and slide numbers of two additional images that meet the criteria listed above
Test your knowledge: Apply display advertising
Practice Quiz. 4 questions. Grade: 100%
4. Review: SEM and display advertising
Wrap-up
Video. Duration: 2 minutes
Acknowledgement and Encouragement
I just want to say, great work. I hope you’re feeling good about all the progress you’re making, learning about search engine marketing and display advertising. If you feel like it’s hard, that’s okay. This is a lot of new information. Keep up your learning, and your understanding will grow.
Let’s Recap
Let’s recap the topics we’ve covered:
1. Introduction to Search Engine Marketing
- Why advertise in a search engine?
- Google Ads types, including text ads, local service ads, and shopping ads.
2. In-Depth Exploration of Google Ads
- Setting a budget and understanding bidding strategies.
- The role of keywords and how Google ranks ads in the ad auction.
- Step-by-step guide on creating a Google Search Ad.
3. Dive into Display Advertising
- The rationale behind display advertising.
- Different types of display ads available.
- In-depth analysis of responsive display ads from Google Ads and how to optimize them effectively.
A Broader Perspective
As a digital marketer, even if you aren’t working directly in search engine marketing or display advertising, it’s essential to understand how each method works and its potential costs. For instance, you might need to help an organization determine where to allocate their ad budget – whether in SEM, social media ads, or traditional advertising like magazine ads. Deciding the best advertising strategy to help the organization reach its goals might fall within your purview.
Conclusion
You’ve done some excellent work, and I hope you’re proud of the progress you’ve made so far. You’ve demonstrated a real commitment to learning about search engine marketing and display advertising, and you are well on your way to becoming job-ready.
Glossary terms from module 4
Reading. Duration: 20 minutes
Terms and definitions from Course 2, Module 4
- Open Link to access Glossary module 4
Module 4 challenge
Due, Nov 12, 11:59 PM WET. Quiz. 10 questions. Grade: 100%
5. Course review: Attract and engage customers with digital marketing
Course wrap-up
Video. Duration: 3 minutes
I just wanted to say, congratulations on completing this course on attracting and engaging customers through digital marketing. You should be really proud of how far you’ve come.
Let’s Review What You’ve Learned
Let’s take a moment to review all you’ve learned in this course:
-
Customer Persona:
- Importance of creating customer personas.
- How to create simple personas for your ideal customers.
-
Marketing Funnel:
- Understanding the four steps: awareness, consideration, conversion, and loyalty.
- Learning strategies and tactics at each step, including:
- Search engine marketing.
- Email marketing.
- Remarketing.
- Testimonials.
-
Search Engines:
- How Google Search works.
- Keyword research and building a keyword list.
- Site structure and website organization.
- Search engine optimization (SEO) for visibility.
-
Online Advertising:
- Benefits of search engine marketing.
- Different ad formats.
- Best practices for reaching your marketing goals.
- Introduction to display advertising.
- Creating effective responsive display ads.
What’s Next: Social Media Marketing
In the next course, you’ll continue your digital marketing journey with social media marketing and advertising. It’s an extremely fun field!
Overcoming Challenges
I had such a wonderful time teaching you about the marketing funnel, SEO, and SEM. I can’t tell you how much of a privilege it was to support you on your career journey. I want to remind you that it’s natural to face challenges when learning new things, and sometimes it may feel overwhelming. But remember, you can do it.
Dedication Pays Off
Be proud of yourself for finishing this course. It wasn’t easy; it took dedication and consistent hard work. As you move forward, remember the commitment you’ve shown to get to where you are today.
Wishing You Success
I hope you have an exciting new career ahead of you and that you make a positive impact on people’s lives through your work. My name is Coach AK, and that’s all we have for today. Take care and good luck!
Course 2 glossary
Reading. Duration: 20 minutes
To use the template for this course item, click the link below and select “Use Template.”
- Open Link to access Course 2 Glossary
Your learning journey
Discussion Prompt. Duration: 10 minutes
Now that you have an introductory understanding of digital marketing, what is something that you have an interest in that you receive digital marketing about? Please include a written response of 3–5 sentences.
As I’ve delved into the world of digital marketing, I’ve developed a keen interest in learning more about content marketing strategies. The idea of creating valuable, relevant content that not only attracts an audience but also engages and converts them is fascinating. I’m curious to explore the nuances of crafting compelling content, optimizing it for search engines, and leveraging various digital channels to reach a wider audience. Content marketing’s role in building brand authority and establishing trust with customers is something I find particularly intriguing, and I look forward to deepening my knowledge in this area.
END! - Week 4 - Course 2
Final Grade of this course: 90.00 %