Week 3
Ads and campaigns in e-commerce
You will discover how to reach customers online through methods like advertisement campaigns and examine the benefits of online advertising. Then, you’ll explore how seasonality affects e-commerce businesses. Finally, you’ll learn how to optimize an e-commerce marketing strategy to meet campaign goals.
Dedication to study
-
Videos: 38 min
-
Leitura: 2 h 40 min
-
Teste: 1 Teste com avaliação
Learning Objectives
- Explain the uses and benefits of online advertising for e-commerce.
- Use Google Ads to engage e-commerce customers.
- Define what Smart Campaigns and Smart Shopping campaigns are.
- Explain how trends and seasonality affect e-commerce businesses.
- Optimize e-commerce campaigns and strategies.
Content
- Ads in e-commerce
- Google shopping campaigns
- E-commerce trends and seasonality
- Review: Ads and campaigns in e-commerce
1. Ads in e-commerce
Welcome to week 3
- Video Duration: 1 minute
Building an e-commerce store is one of the first steps to sell online. But then what? Customers don’t automatically show up because you built a store. You need to use specific strategies to drive traffic to your store. One of the ways to do that is through online advertising, which you’ll learn about in this part of the course. Let’s review what’s been covered in this course so far. First, you got an overview of e-commerce stores and how they work. Then you learned how to use Shopify. You also learned how to connect an e-commerce store to Google and other shopping channels. So, what’s coming up next? First, you’ll learn about the benefits of online advertising. Next, you’ll learn how to use Google Ads to connect with your e-commerce customers. After that, you’ll discover the basics of Google Smart campaigns. You’ll also learn how to create a Smart Shopping campaign. Next, you’ll explore seasonality in e-commerce and how to use Google Ads to plan for seasonality. Finally, you’ll learn how to optimize your e-commerce marketing strategies. Learning how to drive traffic to an online store is an important skill to learn if you want to work in e-commerce. You may be involved in creating advertising and marketing campaigns for your future employer. Alright, time to get started.
Advertise online
- Video Duration: 5 minutes
I have a question for you: how many advertisements do you think the average person is exposed to in a day? 50? 75? 300, maybe? If you guessed anything below a few thousand, you may be wrong. If you’re a US citizen, digital marketing experts estimate that you can be exposed to anywhere between 4,000 to 10,000 ads each day. Globally, these figures can differ, but this statistic is very telling of the prevalence of advertisements. Now, think about the time you personally spend on the internet. I’m sure a lot of the ads you experience in a day come directly from a computer or phone screen. This type of advertising is called online advertising. Simply put, online advertising is a form of marketing which uses the internet to deliver promotional marketing messages to consumers. Whether a brick-and-mortar store or an online retailer, online advertising is now the go-to method for most businesses’ advertising purposes. It may be hard to believe, but before the mid-1990s, online advertising was largely prohibited on the internet. Companies were forced to rely on traditional advertisements in radio, television, billboards, and magazines. That all changed once the ban was lifted. Online ads soared, becoming the primary way for companies to get their brands recognized and products discovered. Why did so many retailers rush to online advertising? Let’s explore this by going over the four key benefits of online advertising. The first benefit of online advertising is that it’s cost effective. When we compare the two, traditional advertising requires a significantly larger budget than modern online ads. As we discussed in the previous course, these advertisement costs are calculated by CPM, which stands for cost per 1000 impressions. In general, the average CPM for online advertising ranges from approximately three to ten dollars. By comparison, it costs approximately $15 to $30 to reach that same amount of people through newspapers or television advertisements. To improve efficiency, advertisers shifted their advertising budgets to focus largely online. The second benefit to online ads is that they can have global reach capabilities. Before online advertising, reaching a global audience was nearly impossible for small to medium sized companies since global campaigns using traditional advertising could cost millions of dollars and require extensive research. Thankfully, online advertising has the ability to target specific sections of the world using digital marketing technologies. Businesses can now market to an internet user in a completely different country without the cost and hassle that came with traditional advertising. Moving along, the third benefit of online ads is they help advertisers gather data for effective brand strategizing. With traditional advertising mediums like billboards, advertisers have little insight on how effective their advertisements really are, and they don’t know if their billboard is in the right place. For example, a company can put their advertisements on a busy highway to get noticed, but if the traffic is moving too quickly, drivers might not have the time to read them. The business will never know for certain how many people paid attention to their advertisement or what percentage of those people searched for their company based on that advertisement. Online ads are different. Many times advertisers can track analytics to see where their ads were seen, how many people clicked on those ads, and how many of those clicks lead to a purchase. This data is important for determining where to spend advertising dollars. And the fourth benefit of online ads is they are quick and easy to produce. Traditional media forums can require a lot of work. For example, if a company wants a television ad, they may have to hire actors, write a script, and pay for a production crew. This takes time, additional expenses, and detailed planning. Online ads bypass most of these complications by having automated structures that streamline the process. Depending on the ad hosting service, advertisements will require companies to simply input information and generate their desired ad. Later, we will explore one of those automated systems. These four benefits of online advertising are just a start. When you enter the e-commerce field, you’ll recognize more benefits that will come with online ads. Today, the most common types of online ads are powered by Google Ads. With Google being the most popular search engine globally, Google Ads allow internet users and consumers to search, browse, and compare products across a wide variety of brands and retailers. Coming up, you’ll learn about how Google Ads use campaigns to connect with customers. Meet you there.
Platforms for e-commerce ads
- Reading Duration: 20 minutes
Whether you’re helping to launch a new e-commerce store or working for a thriving e-commerce business, one of the best ways to acquire new customers is through e-commerce advertising. E-commerce advertising is any form of online or offline advertising that raises awareness of and drives traffic to an e-commerce business. E-commerce advertising—along with other digital marketing tactics—can help support any e-commerce marketing strategy. In this reading, we’ll discuss some top online platforms through which to advertise your e-commerce products or services.
Google Ads
If you’ve taken previous courses in this program, you’ve learned how Google Ads can support a business’s digital marketing strategy. Google Ads is an ideal tool for e-commerce businesses that want to boost brand awareness or acquire new customers. Google Ads enables you to show Search ads on Google search engine results pages (SERPs) and place display ads on websites via the Google Display Network. As the world’s biggest search engine, Google’s Search and Display ads have tremendous reach potential.
Google Shopping ads
Google Shopping ads are image-based product ads that show a photo of a product, its title and price, the store name, and any reviews. These ads allow e-commerce businesses to display their products every time a relevant search is made, enabling them to expand their products’ visibility to a wider audience. When a user clicks on an ad, they are taken to the product page in the e-commerce store. Since many people use Google to search for products, Google Shopping ads can help drive traffic and conversions. You will learn more about Google Shopping campaigns in an upcoming lesson.
Google Discovery campaigns
Google Discovery campaigns deliver highly-visual, personalized ads that can be displayed on the YouTube Home and Watch Next feeds, the Discover app, and the Gmail Promotions and Social tabs. Discovery campaigns are designed to reach users who are most likely to be interested in a product or service, as determined by Google’s algorithms. Discovery campaigns can help you drive engagement and conversions because they show relevant, meaningful ads to people when they are most receptive to learning more about a business’s products and services.
YouTube Ads
With more than a billion hours of video viewed daily, YouTube Ads can reach a wide and diverse audience. On YouTube, e-commerce businesses can set up video ads and campaigns that align with their marketing goals and post them on their channel. This can provide these businesses with the opportunity to increase brand awareness and drive traffic to their online store. YouTube Ads are especially effective for sharing educational or informational content, such as product demonstrations, product reviews, or explainer videos.
Amazon Ads
Amazon Ads can help e-commerce businesses connect with potential buyers on a platform specifically designed for shopping. With Amazon Ads, advertisers bid on keywords and placements to show their products higher in search results. This can help businesses get their products in front of a wider audience. Amazon offers a variety of advertising options, including sponsored products, sponsored brands, sponsored display ads, video ads, and audio ads.
Facebook and Instagram Ads
Facebook and Instagram, both owned by the parent company Meta, are incredibly popular social media platforms visited by hundreds of millions of potential customers daily. Ads Manager is an all-in-one tool for creating ads, managing them, and tracking their performance on these platforms.
Facebook Ads
Facebook has the most users of any social media platform, with billions of active accounts. Popular among a wide variety of demographic groups, Facebook Ads can help reach a target audience. Facebook offers a variety of ad formats that may benefit e-commerce businesses. Collection ads, for example, provide videos or images of products from a business’s catalog and allow people to move seamlessly from the discovery of a product to a purchase. Facebook Ads also allows businesses to target customers by location, occupation, interests, past activity, and more.
Instagram ads
On Instagram, e-commerce businesses can create ads in a variety of highly-visual formats—from image-based ads to video reels to stories—to promote their products and connect with their target audience. Instagram ads can be directly linked to a product page or another landing page, giving users a quick and easy way to engage with products.
Pinterest Ads
Like Instagram, Pinterest is a highly-visual platform. With Pinterest ads, brands can advertise their products through promoted ads appearing as pins in the organic search results.
TikTok For Business
TikTok For Business offers e-commerce businesses an opportunity to promote their products to a young, highly-engaged audience. Influencer marketing is a key component of advertising on TikTok, and TikTok’s Creator Marketplace helps brands find influencers to partner with.
Twitter advertising
Twitter is a social media platform primarily used for breaking news and engaging with influencers and celebrities. Twitter ads offers two options: Quick Promote, which automatically promotes Tweets an advertiser chooses to their target audience, and Twitter Ads. Twitter Ads campaigns are objective-based, meaning they are optimized towards the objective the advertiser selects, and they are only billed for actions aligned with that goal.
Key takeaways
Advertising allows e-commerce businesses to reach people who may or may not be familiar with that business’s products or services. The goals of e-commerce advertising campaigns can include everything from growing brand awareness to increasing conversions. An advertising platform that works well for one e-commerce business may not work as effectively for another, so advertisers should test on each before launching campaigns. Generally, using a mix of platforms to place online ads is likely to yield the best results.
Using videos in ads
- Reading Duration: 10 minutes
Previously, you learned about using various advertising methods online through e-commerce ad platforms. In this reading, we’ll learn about digital advertising, only this time, we’ll cover video ads specifically.
Digital advertising vs digital marketing
Digital marketing is the practice of reaching consumers online through digital channels with the aim of turning them into customers. Digital advertising is the practice of promoting a brand and generating sales through the use of ads. Using video in ads is one effective tactic of digital advertising.
Benefits of digital advertising
Videos are an effective way to advertise for a number of reasons. For starters, 4 billion videos are watched on YouTube everyday. That’s billions of potential opportunities for a video ad to be seen. It’s also estimated that almost one-third of shoppers purchase a product after encountering a video ad, which is a conversion rate of 33% — well over most average ad conversion rates.
There are other benefits, too. A video can deliver more information than a graphic or a photo can. The use of videos can add a personal touch to a brand’s ads, and videos sometimes do a better job of showcasing products than images do. Using ads that include storytelling videos, testimonial videos, or influencer review videos are all great ways to take your brand awareness to the next level.
Types of ads
There are many kinds of ads you can use in digital advertising. By now, you may be familiar with some of them. Using ads on display networks, social media, search engines, or video streaming platforms (like YouTube), can boost a business’ ability to reach potential customers.
Ad-hosting platforms
There are all kinds of ad-hosting platforms available to digital marketers, and in order to best serve your target audience, you should be familiar with as many as possible. Below are some examples of spaces you can place ads within.
-
Facebook and Instagram are social media platforms where you can run ads that appear in people’s social media feeds or in their stories.
-
Placing ads on Google Ads will allow them to be seen while people are browsing for similar products.
-
YouTube Ads, which exist before, in the middle of, and after videos on YouTube, give your brand visibility through their video platform. These ads pop up in the same media player they’re using to watch videos.
This isn’t an exhaustive list — if you want to find additional ad-hosting platforms, you’ll want to do some more research. There are many other platforms for e-commerce ads, but remember that some of them aren’t always well-suited for videos. Where you place your video ads matters.
Setting your strategy
Before you create a video ad, you’ll want to make sure you set your strategy. When you’re setting your advertising strategy, ask yourself: where will these ads be placed? Who is my target audience for these ads? What is my plan if the ads don’t perform well? Will there be one ad or will we create a whole campaign of video ads?
Knowing this information will help you stay on track. As a digital marketer or digital advertising professional, remember that there will always be some level of trial and error. Be prepared to pivot or try new things if your video ads aren’t generating sales or creating brand awareness like you wanted them to.
Tips to optimize digital advertising
After you’ve set your digital advertising strategy and answered the questions above, you can start executing your video ads.
When creating video ads, here are some aspects to consider:
-
Length. Video ads should only run for about 20 to 30 seconds at most. The average viewer isn’t likely to watch for much longer than that. In some cases, your ads may only be a few seconds long. The length of your video will depend on your goals and your intended audience.
-
Hook. The first 3-5 seconds are where you really catch the attention of your potential customer. Make sure you add content that hooks them right away.
-
Size and dimensions. Depending on where you plan to run your ads, the size and dimensions of your videos will be different. For instance, ads on Instagram should be 9x16 or square, whereas ads on YouTube should be 16x9.
-
Target audience. Create videos your potential customers will like, and place the ads wherever your potential customers are most likely to be, whether that’s on social media, driving by digital billboards, watching videos on YouTube, or somewhere else.
Helpful tools to make video ads
There is data that suggests videos these days don’t have to have the highest production value. This is good news if you’re just getting started — you can make video ads from anything!
Some tools that will help you are:
-
Soapbox (if you use Google Chrome)
Key takeaways
Digital advertising, or the practice of promoting a brand and generating sales through the use of ads, is an integral part of digital marketing today. Understanding how to strategize for, execute, and run video ads, increases your chances of growing your brand and generating sales. There are endless ways to create video ads, and there are a multitude of tools to help you along the way.
Test your knowledge: Basics of online ads
- Practice Quiz. 4 questions. Grade: 100%
How did an online ad get your attention?
- Discussion Prompt Duration: 10 minutes
Compared to television or billboard ads with high-cost and long lead times, you’ve learned that digital ads can be created at a fraction of the cost using streamlined and automated processes. As a result, you’re possibly exposed to hundreds of online ads each day.
Think about an online ad that you’ve recently encountered and consider the following questions:
What was most noticeable about the online ad?
If the online ad was for a product, what was most memorable about the product? Or, were creative elements of the online ad more memorable than the product itself?
Please write 3–4 sentences (60–80 words) as a response to this prompt. Then, applying what you’ve learned about digital ads, comment on at least two posts from other learners.
Answer
The online ad that recently caught my attention was particularly noticeable due to its vibrant color scheme and eye-catching graphics.
The use of bold typography and compelling visuals immediately drew my focus.
While the product being advertised was intriguing, what stood out most was the creative execution of the ad itself—capturing my interest through dynamic design and a well-crafted message.
I think this highlighted the effectiveness of visually striking digital ads in capturing audience attention amidst the daily online advertising barrage.
2. Google shopping campaigns
Advertise with Google Ads campaigns
- Video Duration: 6 minutes
If you listen to music online, you may have noticed that when a famous musician releases a new song, their new music video might appear in the “recommended” section when you visit YouTube. Or, you may notice a link to their website in the ads on Google Search pages. That isn’t a coincidence. It’s a Google Ads campaign hard at work. A campaign is a tool that creates and initiates a plan, for how to promote products or services on Google’s vast network of search results, websites, videos, mobile apps, maps, shopping listings, and more. To create that plan, campaigns use a set of ad groups like ads, keywords, and bits. These groups share a budget, location targets, and specific audiences. Google Ads offer a variety of campaign types to help you craft specific messaging in your online ad to attract and engage potential customers. For example, app developers use App campaigns to find new app users and increase sales within their app. The campaign helps them promote their app on many channels. Working in the field of e-commerce, you’ll likely encounter four types of ad campaigns that fit your business needs and help you reach your audience. They are: Shopping, Search, Display, and Video. In this video, we’ll discuss each of these ad campaigns one-by-one and when they are commonly used. Let’s get started with Shopping campaigns. Shopping campaigns are product listings that appear on search results and the Google Shopping tab. They’re ideal if you’re an e-commerce retailer looking to sell your product inventory. Shopping ads show users a photo of your product, plus a title, price, store name, and more. Products will also appear on the Shopping tab along with their competitors. Customers find this helpful for comparing the appearance and price of similar items. For retailers, this could benefit or harm sales. If your product has great quality and is affordable, it is more likely to sell over products that have a poor appearance or are too expensive. Using Shopping campaigns are an essential part of the online buying and selling process. If you’re a retailer you can use Shopping campaigns to promote your online inventory and boost traffic to your website store. They help with retail marketing by using visually engaging product listings to promote your retail products. They also help boost your sales by getting people to buy on your online store or sign up for more. Next are Search campaigns. You may remember learning about Search campaigns in an earlier course. As a reminder, a Search campaign is text ads on search results that appear while people search on Google for related products and services. Search campaigns help reach customers who know what they are looking for and are ready to make a purchase. For example, picture this: a busy restaurant manager named Jamie forgot to order her partner flowers for their wedding anniversary, a tradition they’ve held for the last 20 years. During her hectic day, she goes to Google Search and types in “flowers” But there’s a problem. She’s met with nearly seven billion search results. Jamie is overwhelmed and has to spend a significant amount of valuable time filtering through the endless results. Search campaigns quickly help identify solutions to searches. If a florist in Jamie’s area used a Search campaign, she would’ve been able to quickly identify a florist who offers same-day delivery service at the top of the web page. This would have made it easy for her to place an order and return to work. Both Search and Shopping campaigns run using a PPC, or pay-per-click, model. You may remember that this is a marketing strategy where a company only pays for the ad when somebody clicks on it to visit the company’s website. Next are Display campaigns. If you’ve been taking the courses of this program in order, you may have already discussed these types of ads in a previous section. As a reminder, a Display campaign is a Google Ads tool that allows businesses to place an image advertisement across various websites. Display campaigns aren’t limited to the Google Search platform. They can appear on any platform that’s part of the Google Display Network. The Google Display Network is a group of more than two million websites, videos, and apps. The Google Display Network sites reach over 90 percent of Internet users worldwide. Think of these ad campaigns as digital billboards. Unlike Shopping campaign ads, Display campaigns are often artistic and use a combination of art, graphic design, photography, and typography to promote their products. Another type of campaign commonly used in e-commerce is Video campaigns. YouTube has over 2.3 billion users worldwide as of 2021, according to a recent report. With so many users constantly streaming videos, e-commerce specialists have a valuable opportunity to reach new and returning customers using video advertising. A Video campaign is a Google Ads tool that allows businesses to place video advertisements before, during, or after YouTube videos and in the search results. What are the specific benefits of Video campaigns? Just as search campaigns help businesses get noticed on Google, Video campaigns help businesses and products get noticed on YouTube. Like Display campaigns, Video campaigns help your potential customers meet your e-commerce products at the start of their buying journey and help spread awareness about your brand. They can also remind returning customers to revisit your products or services. These video ads have a limited time to make an impression on the people who are watching them. Oftentimes a lot of work has to go into them to ensure that they are engaging. Lots of e-commerce businesses hire advertisement agencies or professional video producers to make these ads for them. This is something you may have to consider in the future, depending on the size and needs of the companies you end up working for. Search campaigns, Shopping campaigns, Display campaigns, and Video campaigns are regular Google Ads campaigns. When you use any one of these types of campaigns you have complete control of the campaign’s specific goals, keywords, conversion metrics, and budget decisions. While Google Ads campaigns require knowledge to use, they can be extremely beneficial when creating an ad campaign. Coming up, you’ll learn more about how to run successful campaigns.
Test your knowledge: How to place online ads
- Practice Quiz. 5 questions. Grade: 100%
Understand Smart Campaigns
- Video. Duration: 4 minutes
While regular Google Ads campaigns can be helpful, they require some advanced knowledge and skill to manage. Luckily, there are Smart campaigns. A Smart campaign is an automated campaign management tool within Google Ads that helps you promote your business. Originally called Google AdWords Express, Smart campaigns were designed for small businesses and new advertisers. They provide a simpler business marketing experience by combining Search and Display campaigns and allow Google to control most of the campaign’s management. As an entry-level e-commerce specialist, there are some significant advantages to using Smart campaigns. First, Smart campaigns are automated. When you create a Smart campaign, you give Google control over the direction that your campaign goes and how your budget is spent. This means that you can spend less time checking in on your campaign while it operates. Second, they’re easier to set up. Smart campaigns can be set up in under 15 minutes since they only require a few steps to complete. In comparison, regular campaigns require more steps to set up. Later on in this lesson, you will learn these steps as we create a Smart campaign. Lastly, Smart campaigns save money. Remember when we learned that all Google campaigns run using a PPC, or pay-per-click model? While regular campaigns rely on you to determine the best budget strategies, Smart campaigns use detailed analytics and data to determine the highest conversion rate. That means people who click on your ad will be more likely to buy your product, reducing the gamble of having to pay when someone clicks on your ad, but doesn’t make a purchase. While Smart campaigns are less complex than regular Google Ads campaigns, there are some control limitations, including limited campaign goals, limited keyword options, and limited control of the budget. Like regular Google Ads campaigns, there are different types of Smart campaigns. For e-commerce, Smart shopping campaigns are the best Smart campaign to help maximize shopping potential. A Smart Shopping campaign is an advanced shopping campaign that uses technology to optimize for more sales and reach Google shoppers across Google’s sites and networks. After just a few steps, Google will optimize to show your inventory to the right customers at the right time across different networks, including the Google Search Network, Google Display Network, YouTube, and Gmail. To accomplish this, Smart Shopping campaigns optimize real-time signals like user queries, time of day, and devices to show your products to customers who are more likely to buy your products. A study found that Smart Shopping campaigns have over 20 percent more conversion value than regular shopping campaigns. There are three key benefits of Smart Shopping campaigns. First, Smart Shopping campaigns optimize existing shopping ad products. They combine your single existing product feed and assets into ads across a variety of networks. Google systems test them and display the ones that perform the best. Second, they leverage automatic bidding. Google analyzes and intelligently predicts the value of a potential conversion every time a user searches for products or services you’re advertising. Then it automatically adjusts your bids for these searches to maximize your return on them. The third benefit for Smart Shopping campaigns is that you can get started right from your e-commerce platform, since they allow easy integration through a third-party platform, like Shopify or WooCommerce. Coming up, you’ll continue to develop your knowledge of e-commerce concepts and practices. Get ready.
Prepare a Google Shopping campaign
- Reading Duration: 20 minutes
Before launching a Google Shopping campaign, you’ll need to complete a few requirements. This reading will review some of those requirements, including setting up Google accounts, reviewing policies, and completing product information.
Set up Google accounts
Before you can begin a Shopping campaign, you’ll need to set up accounts with Google Merchant Center and Google Ads and link them together. Linking your Google Analytics property to your Merchant Center account allows you to access Merchant Center-specific reporting or insights to help improve your campaign’s performance.
If you have already done so, confirm that the two accounts were linked correctly. To refresh your knowledge of Google Merchant Center and Google Ads, revisit an earlier video on this subject.
Review policies
Your content for Shopping campaigns and Shopping ads needs to comply with the Shopping ads policies. These policies are divided into four general categories:
-
Prohibited content: Content you’re not allowed to promote on the Google Network
-
Prohibited practices: Things you can’t do if you want to advertise with Google
-
Restricted content: Content you can advertise, but with limitations
-
Editorial and technical requirements: Quality standards for your ads and website
Before launching your campaign, it’s important to check that you are not violating any of Google’s Shopping ads policies. If you do, your Shopping campaign may be ended involuntarily.
For a complete list of all Google policies, visit the Google Ads policies website.
Complete product information
Review your product information in Merchant Center programs, and edit it if necessary. Submitting your product data to Google correctly is essential for creating successful product ads. Google uses this data to make sure that it’s matched to the correct queries.
Product information includes:
-
Basic product data: This informs shoppers what they are purchasing. The product information you submit such as IDs, product titles, product descriptions, and links are the foundation of a successful Shopping ad campaign.
-
Price and availability: These attributes define the price and availability for your products.
-
Product category: This helps organize your advertising campaigns in Google Ads and to override Google’s automatic product categorization in specific cases.
-
Product identifiers: These attributes such as the Global Trade Item Number and Manufacturer Part Number are used to define the products you’re selling in the global marketplace.
-
Detailed product description: These attributes are used to submit product characteristics that users commonly search for, such as color, condition, and material.
-
Tax information: Use this setting to override the account tax settings for an individual product. You can submit tax information for all your products using the account settings in the Merchant Center.
For a full list of product information, visit the product data specification page on the Google Merchant Center website.
Key takeaways
You must complete certain requirements to prepare your Google Shopping campaign. Carefully following these guidelines will ensure that you are on the right path for a successful Shopping campaign that keeps your customers in mind.
Create a Smart Shopping campaign
- Video Duration: 1 minute
You’re ready to learn how to create a Smart Shopping campaign. Remember, setting up a Smart Shopping campaign takes under 15 minutes. This is significantly less time than regular campaigns. Like I mentioned previously, I don’t expect you to create your own Shopping campaign during this program. This video is to give you a chance to explore what it’s like to create your first campaign in the future. I’ll start by signing into Ads.google.com. Next, I’ll select the campaigns menu and add a new campaign. Here, I can decide my campaign goals. If you want to create a regular campaign that I can control 100 percent on my own, I would click, choose that option here. But since I’m creating a Smart Shopping campaign, I’ll select the Sales as the goal for your campaign instead. Then Shopping. Next, I’ll select my Merchant Center account. If for any reason I hadn’t linked my Merchant Center account with my product data, I’d have to do so now. But luckily, I’ve already completed that step. For campaign subtype, I’ll select Smart Shopping campaign, then “Continue” I’ll enter the name of my campaign and the campaign’s average daily budget. By default, Smart Shopping campaigns set bids that maximize the value of your conversions within your provided average daily budget. Now, it’s time to choose specific products or groups of products that I’d like to advertise in my campaign. If you don’t specify products, your entire feed will be eligible to appear in your ads. This could reduce their specificity and worsen their performance. Finally, I can preview my Ad and then select “Save” and I’m done. You’ve just witnessed what it’s like to create a Google Smart Shopping campaign. You can use the Google Ads website to explore more advanced campaigns that may fit your business needs.
Disapprovals in Google Ads
- Reading Duration: 20 minutes
Regardless of the campaign type, all of your ad content needs to comply with Google Ads policies. If your ad violates these policies, it will be disapproved and won’t run. Familiarizing yourself with Google Ads policies and creating ad content that adheres to them can help reduce the likelihood that your ad will be disapproved. Even if you do this, you may occasionally have ads that are disapproved. In this reading, we will discuss Google Ads policies and some examples of violations of them, error and warning checks that indicate an ad may be disapproved, and how to fix a disapproved ad.
Overview of Google Ads policies
Google Ads policies are designed not only to follow laws but to ensure a safe and positive experience for users. These policies aim to prohibit content that could be harmful to users. Google Ads uses a combination of automated and human evaluation to ensure ads comply with these policies.
As you learned in a previous reading, these policies are divided into four general categories: prohibited content, prohibited practices, restricted content, and editorial and technical requirements. Below is a description of each of these categories and examples of violations of them:
-
Prohibited content: Content you’re not allowed to promote on the Google Network
- Examples: Ads that contain counterfeit goods, dangerous products or services, or inappropriate or offensive content
-
Prohibited practices: Things you can’t do if you want to advertise with Google
- Examples: Ads that contain malicious software, collect data without appropriate disclosures or security measures, or misrepresent products or services
-
Restricted content: Content you can advertise, but with limitations
- Examples: Ads that contain sexual, political, alcohol, or gambling-related content or are geared at kids
-
Editorial and technical requirements: Quality standards for ads, websites, and apps
- Examples: Ads that do not meet certain technical, formatting, or editorial requirements
Before creating an ad, review Google Ads policies to help ensure your ad is in compliance with them.
Error and warning checks
Google Ads Editor automatically detects certain issues that might cause your ad to be disapproved. As you edit your ad, red error icons or yellow warning icons appear to indicate any potential problems. For example, if your ad contains capitalization that is not used correctly or for its intended purpose (e.g., COFFEE, COFfEE, C.O.F.F.E.E.), Google Ads Editor will show a red error icon next to the affected row.
The following icons indicate the status of your ad:
An icon with an exclamation point in a red circle indicates an error. Google Ads Editor can’t check or post the affected item unless you request an exception or make the required change.
An icon with an exclamation point in a yellow triangle indicates a warning. Warnings don’t prevent an item from posting, but you should check the item for accuracy and to ensure that it meets Google Ads policies.
A green circle icon appears after you check your changes, and it indicates that the item has passed Google Ads policy checks.
Ad review process
After you create or edit an ad or extension, the review process begins automatically. The content in your ad—including your headline, description, keywords, destination, and any images and video—will be reviewed. Most ads are reviewed within one business day. However, some reviews take longer if the ad requires a more complex review.
-
If your ad passes the review, its status will change to eligible, and it will start to run.
-
If the review indicates that your ad violates a policy, its status will change to disapproved, which means it can’t show anywhere.
-
If your ad is marked eligible (limited), it will not show in certain regions, to certain age groups, or on certain devices.
Fix a disapproved ad
If any of your ads are disapproved or eligible (limited), your ad may not be able to run until it’s corrected. In Google Ads, this will be noted in the status column, where you can also find out what policy violation is impacting your ad.
When you have an ad with policy violations, review the policy and then edit the ad so that it complies. Once you fix your ad, Google will review the ad and allow it to run if it’s determined to be compliant.
This video provides more information about how to fix a disapproved ad.
If you’ve reviewed the policy and still believe your ad is compliant, you also have the option to file an appeal. Scroll down to the Appeal policy decision section of this article for more information.
Key takeaways
Learning about Google Ads policies around prohibited content, prohibited practices, restricted content, and editorial and technical requirements can help you create content that is in compliance with these policies, reducing the likelihood that your ad will be disapproved. If there is still an issue with an ad you’re editing, a red warning icon will indicate that there is an error you need to fix. If the review of your ad determines that it violates a policy, its status will change to disapproved. You will need to review the policy violation and fix the error before your ad can run.
Resources for more information
-
Why is my ad disapproved?: This video describes some common reasons Google Ads are disapproved and how to fix them.
-
19 Pesky Google Ads Disapprovals and How to Fix Them: This article describes how to fix the causes of common Google Ads disapprovals, appeal a disapproval, and avoid future disapprovals.
3. E-commerce trends and seasonality
Explore seasonality in e-commerce
- Video Duration: 6 minutes
I have a question for you. When is your favorite time of the year? Is it during the part of the year when your favorite weather, like sunshine or snow, is the most consistent? Or maybe your favorite time of the year correlates to a specific day or event, like around your birthday or an anniversary. Like clockwork, these periods come around year after year. Believe it or not, digital marketers and e-commerce specialists anticipate their own special times of the year based on past patterns. This concept is called seasonality. Seasonality, also called seasonal marketing, refers to the regular and predictable fluctuation of e-commerce traffic around special holidays, events, and weather on a quarterly or yearly basis. Those in the e-commerce industry use seasonality to determine when a business will receive a potential increase or slowdown in revenue sales. Seasonality is split into two parts: on-season and off-season. The on-season is the period where customers are much more likely to buy products due to related weather variables or special events. During the on-season, businesses can expect to receive the most financial gain. For example, in countries that experience drastic temperature changes, some clothing items are more popular during certain times of the year than others. This is the case for sandals. While some people may opt to wear them year-round, they are generally purchased and worn during warm weather seasons. This is the sandal industry’s on-season since the industry experiences a period of rapid economic expansion, called a boom. However, the on-season isn’t limited to just seasonal weather. Holidays and special events play a huge role in driving traffic to e-com sites. For example, consider the florist industry. In countries that celebrate Mother’s Day, flowers are a common gift to purchase for maternal figures. Globally, the week leading to Mother’s Day is the busiest week of the florist industry. This is significant because Mother’s Day doesn’t occur in the prime flower-growing season for all countries, yet, it is still a popular item to buy in those countries in celebration of the holiday. Other important e-commerce holidays include back-to-school events and cyber sales week. The off-season is the period where customers tend to take more time in making purchases, especially if it’s for a larger ticket item. The off-season is also a time when businesses experience a period of relatively low site traffic and revenue. Let’s go back to our sandal industry example. During the winter, people choose to wear sandals less due to the harsh weather. This period is generally considered a period of poor performance or inactivity, which is called a slump. It’s important to note that the off-season doesn’t mean that a business has nothing to accomplish. On the contrary, the off-season is one of the most valuable times of the year for businesses to focus on off-season marketing strategies. The goal of off-season marketing is to put your business ahead of the competition by building a strong brand awareness that will directly drive customers to your site during your on-season. Here are a few approaches. The first is to grow your database. During the off-season is the time to target new contacts and attract new audiences. While it may sound strange to create additional campaigns when you are in a financial slowdown, growing your database during the off-season is important. When your new campaign leads to a conversion, you can obtain customer information and use this information to follow up with new promotions during the on-season. Second, increase your social media presence. In order to gain more customers during your peak time of the year, you have to increase your awareness. One way to do that is through social media. Use this time to interact with your customers and create social media posts, engaging content. This helps you stay connected to your customers and leads throughout the year. If you’re curious on how to grow your social media presence, I recommend visiting an earlier course on social media marketing. Third, create quality content. Great content takes time, effort, and creativity to cultivate and make memorable. It’s often measured by how many people interact with it and how much it leads to conversions. This will help your business stand out from the crowd. You can utilize your site’s blog feature to write interesting and thought-provoking posts. This is helpful for building a community that your audience feels connected to. It also builds interest for additional products related to the article. For example, sports is a hobby that connects citizens globally. A soccer apparel company could conduct an interview and post an interview with a professional sports player about their career during the off-season. This article would be a great opportunity for the company to share an interesting story. It can also draw customers to current discounted jersey promotional sales and lead to their brand being remembered during on-season. Another off-season marketing strategy is to promote less popular products on your site if they’re available. Turning the attention to less popular selling products on a business’s site is a great way to keep your business profitable during the off-season since doing so will help recover the revenue loss from the decrease in sales to your popular items. To do this, businesses feature the less known products on their homepage, create marketing campaigns for them, and develop creative branding. Finally, there’s geographic segmentation. Geographic segmentation refers to the grouping of customers with regards to their physical location. This is important since depending on your industry, on-season and off-season may occur at different times and locations. Remember the sandals industry example? Although sandals might currently be in a weak financial period due to cold weather, boots are experiencing an on-season. Using geographic segmentation, a business that sells a variety of shoes might decide to target sandals to potential customers in warm locations in the world and boots to potential customers who are in cooler locations. Okay, that’s it for now. Coming up, we’ll explore more about strategizing to reach customers. I’ll meet you in the next video.
Review: Off-season or on-season
- Ungraded Plugin Duration: 30 minutes
Use Google Ads to plan for seasonality
- Video Duration: 5 minutes
Understanding seasonality is a great way to know what is coming ahead for your business, since it allows you to recognize common trends in your industry. Now that we’ve explored the basics, let’s examine how to use Google Ads to plan ahead of seasonal events. As we mentioned before, Google Ads is an online advertising platform developed by Google where advertisers bid to display brief advertisements, service offerings, product listings, or videos to web users. As an e-com specialist, you’ll likely measure efficiency often and a good time to revisit goals and demand trends is during the off-season. To start, you’ll need to determine your bidding strategy for the on-season or seasonal events. To do this, you’ll use Smart Bidding. Smart Bidding is a subset of automated bid strategies that use machine learning to optimize for conversions or conversion value in each and every auction. To prepare for seasonal events, you can adjust Smart Bidding settings manually or use seasonality adjustments. With the seasonality adjustment tool in Google Ads, you can set a time and date for when you expect to see a short spike in conversion rate. This will inform the smart bid tools when to change its bidding behavior. For example, imagine that a small business owner in Singapore creates festive party decorations. Her business has been open for five years and sales are steady year around. However, she notices every Lunar New Year, a time of great celebration for her city, the demands for her decorations spike for an entire week before the celebration begins. This year, in anticipation of this spike, the owner of the company can build a seasonality adjustment that increases the conversion rate by up to 50 percent for the days leading up to the new year celebrations. Once the period is over, Smart Bidding will immediately go back to pre-sales performance. With Smart Bidding, you can choose which automated target strategy you want to go with. The first Smart Bidding strategy is to maximize your conversion value, or CPA. This is a fully automated bidding strategy, which means that Google will adjust your bids automatically to give you the highest number of store visits. Be aware that this strategy will always spend the full daily allotted budget. So if you have multiple shopping campaigns, you’ll need to decide if each campaign should have their own daily budget assigned or one shared budget. You wouldn’t want all of your budget to be spent on one campaign. The second Smart Bidding strategy for shopping campaigns is to set your return on ad spending, also called ROAS. It means that Google will optimize your bids based on your daily budget to meet the target that you set. With ROAS targeting, if Google Ads determines that a user search is likely to generate a conversion with high-value, target ROAS will bid high on that search. If it determines that the search isn’t likely to generate a high value conversion, it’ll bid low. For this strategy, Google needs to have enough previous conversion data to be able to make smart decisions. This will depend on your previous activity. If you don’t have enough conversion data, then the algorithm can’t make informed decisions. If you choose a ROAS strategy, remember to start off with a realistic target and with a goal a little lower than what your performance has been recently. Then slowly raise the target over time to achieve a more profitable ROAS. No matter which strategy you go with, you’ll need to consider new customer acquisition. With the increase of e-commerce activity beginning in 2020, customers are more willing to try new brands and products. Historically, holidays have been a great time to gain new customers. Google Ads has options for you to plan ahead for that. Under the Settings menu, you can choose your conversion goals in the settings of your campaign. You can add the value that your new customers are worth versus your old customers. This way, the campaign will optimize more for sales for new customers. Okay, now that you know how to use bidding strategies and focus on converting new customers, the next step is using the Google Ads Performance Planner to prepare for the on-season. As you know, during certain periods of the year, consumer intent can be higher, which means customers know what they want to buy. For example, during the winter, instead of waiting around to see an ad for a new coat, customers are more likely to search for a new coat directly on the internet. This leads to more conversions for winter apparel business. The Performance Planner is a tool that allows you to forecast the impact of different spending scenarios and events during upcoming seasons. It also allows you to determine perfect bid and budget settings for campaigns that run year-round. How does it work? It examines previous campaign performance and seasonal trends for your target industry and region. Using the performance tracker, you can set the conversion rate estimate to match the one for the prior year during this time. Or you can also set a custom conversion rate at the planned level. You can even individually define conversion rates for relevant campaigns in your plan. The choice is yours. Have fun planning. For information on getting started with your own Google Ads seasonal planning, be sure to check out the readings in this course.
Test your knowledge: Seasonality in e-commerce
- Practice Quiz. 5 questions. Grade: 100%
Marketing for special events and holidays
- Reading Duration: 20 minutes
In a previous video, you learned that seasonality refers to the regular and predictable fluctuation of e-commerce traffic around special holidays, events, and weather on a quarterly or yearly basis. This reading will continue to develop your knowledge of seasonal marketing and help you understand the importance of planning for “special events” and holidays to increase traffic to your business.
Understanding geographic segmentation
When considering holidays and special events, an online business must start with a sense of where their audience is located. Earlier, we discussed that a target market is a group of customers at which a business aims its marketing efforts and resources. You’ll use this as an indicator of who your audience is and what they care about on a large scale.
For example, in the United States, “Black Friday” is the single busiest shopping day for retailers. It occurs the Friday following the United States’ Thanksgiving holiday, and includes massive discounts and sales on retail products. Knowing whether or not your audience is located in the United States is helpful for marketing to that audience. If a company’s target market is in a country that does not participate in Black Friday, having a campaign marketed for Black Friday may not gather the desired attention.
Holidays and events
Once you’ve identified where your target audience is located, it’s important to identify popular holidays and special events. Identifiers of popular holidays include religious observances, cultural happenings, and education events. The following are a few holidays that are often used to promote sales in many parts of the world.
Some events are specific to regions or cultures
-
Diwali: Also called the festival of lights, Diwali’s exact dates of celebration change annually, based on the position of the moon. A quick Google Search will provide you with the day it is to be celebrated each year. It’s arguably the most widely celebrated holiday in India, although Hindus around the globe make time to celebrate it.
-
Black Friday: One-day super sales event on the Friday following Thanksgiving in the United States.
-
Singles Day: Celebrated on November 11th, Singles day is an unofficial Chinese holiday and shopping event that celebrates people who are not in relationships.
Annual events celebrated across regions and cultures
- “The holiday season”: An annually occurring period of time recognized in many Western and other countries that is generally considered to run from late November to early January.
Some events are annual and celebrated across regions and cultures
-
New Year celebrations: This is the time or day at which the new calendar year begins. Much of the world celebrates January 1 as the start of their new calendar year. Additionally, there are many New Year variations that honor specific cultures or religions happenings, such as East Asian celebrations of the Lunar New Year, Rosh Hashanah, and Songkran.
-
Back-to-school: The period in which students and their families purchase school supplies and apparel for the upcoming school year.
-
Mother’s Day and Father’s Day: These are holidays honoring parenthood and parental bonds. Dates for Mother’s day and Father’s day differ by country.
Planning for events
Once you discover which events you want to plan for, take the following steps into consideration.
1. Create a promotional calendar
Creating a promotional calendar is a great way to identify dates you anticipate an increase in sales and potentially want to create promotional events for your business. Build a list of important holidays and special events, then connect those holidays and special events to specific periods of time ahead of the holidays and special events that you will likely see an increase in traffic.
For example, if children in the Paris, France area usually begin a new academic year between September 2nd and September 9th, a school supply retailer whose target audience is located in Paris will first mark those dates on a calendar.
Then, they’ll decide when is the best time to promote their items. Based on research and trends, they discover that back to school sales activity occurs most between July 20th and July 28th. They’ll mark these days on their calendar. In a future reading, you’ll learn about Google tools where these dates will become handy for marketing.
2. Choose additional marketing and promotional tactics
Earlier in the program, you learned about digital marketing techniques to promote your brand like social media and email marketing. When creating a plan for your holiday or special event, choose which of these marketing and promotional tactics will be most effective. This can vary depending on the types of products or services your business offers but ultimately should fit your audience.
For example, social media marketing is a great way to reach new audiences during the holiday season. However, certain social media sites like Instagram or TikTok tend to have younger audiences than other platforms like Facebook or YouTube. With this knowledge in mind, you can easily make a decision on which marketing or promotional tactic will fit your audience best.
3. Assign specific promotions to each holiday or occasion
During this step, you can decide what specific sale or promotion you want to assign to a holiday or special occasion. Do you want to provide 50% off of an entire purchase? Or, do you want to offer free shipping on all orders over $50 USD?
You can do this by ranking the holidays and events you expect the most gain in traffic to your site and adjust your yearly advertising budget accordingly. Using preselected holiday and special event dates allows you to create a balanced budget for the sales you expect for your business to have. You’ll be able to capture your audience’s attention while also being mindful of your return on investment.
You should also be sure to be competitive among your competitors. If you have the least generous promotions compared to your competition, chances are you may lose out on potential sales.
4. Prepare inventory
And finally, prepare your inventory stock months in advance to plan for the natural increase of traffic to your site. In addition to losing out on potential revenue, running out of stock during holidays and special events can be viewed as unfavorable to potential customers. Analyze sales data and stock up on products that are most popular on your website.
To be mindful of creating a surplus of merchandise, most retailers loosen efficiency goals during the on-season. For example, if a company reduces the sales efficiency goals by 20% during the holidays, they are likely to sell more products sooner and avoid having too many products during the off-season, which they would potentially have to discount significantly more to sell.
Key takeaways
Understanding who your customers are allows you to decide what is important to them. Once you have a grasp on the holidays and special events that they care about most, you can easily begin to create a plan for how you can market your products successfully when it matters most.
Optimize your e-commerce marketing strategies
- Video Duration: 5 minutes
At some point or another, every e-commerce specialist must evaluate what they can do to boost traffic on their site and get customers to buy. Now that you know more about planning for seasonal trends and events, it’s time to learn about how to improve your e-commerce sales efforts. In this video, I’ll guide you through a few effective techniques e-commerce specialists use to optimize their e-commerce strategy. The first is to conduct more research on the industry’s booms and slumps. Knowing when you’ll experience a spike or a slowdown in e-commerce traffic is vital for planning ahead. One way to determine this is by using Google Trends, a Google tool that lets you explore what citizens around the world are searching for on Google. Simply enter words or topics related to your e-commerce products into the interface and you’ll get access to the amount of search interest on that topic. The stats are relative to the highest point on the chart for the given region and time. You can determine how much the word or phrase was searched for. Here’s an example. Remember when I mentioned that Mother’s Day is the busiest day for the floral industry? If a florist wanted to identify another peak day during the on-season, they could type “flowers” in the Google Trends forum. They are met with statistics on the amount of time the word “flowers” were searched in the last year. The largest spike on the chart is around May. As I mentioned before, Mother’s Day is the busiest day for florists and this spike confirms this, since Mother’s Day falls around the month of May in most countries. But can you guess when the second spike happens? The Google Trends timeline suggests that this spike happens around mid February. This correlates with the popular holiday, Valentine’s Day, where loved ones and friends commonly exchange gifts of flowers. This is just an example. Florists and other e-commerce analysts can use this tool to identify other possible peak days for their industry. As you become aware of potential spikes, you can create promotional events that correspond with the spikes to help drive sales. These can include incentives like limited time deals, discounts, or free shipping. The next optimization technique is to simplify the buying process. Have you ever been a shopping cart abandoner? That’s when you start a checkout process for an online order, but never complete the purchase. Lots of time this is due to the complexity of the buying process. You may have had an extremely hard time finding the checkout button, or there may be multiple unnecessary steps to purchasing your product. The process may make you so frustrated that you leave the online store and never return. These issues are called pain points. In e-commerce, a pain point is defined as a specific problem faced by current or prospective customers while interacting with the site. Resolving pain points improves the buyer’s experience with your brand and could help bring customers back to your site. In many cases, companies hire user experience designers to target the issue customers are facing and redesign aspects of their site. As an entry-level designer, you’ll likely be charged with identifying where in the process the shopper decided to leave the shopping experience, also called a shopping cart abandonment. If you own your own e-commerce business, we don’t expect you to hire a user experience designer right away. Instead, many small businesses determine their customers’ pain points by conducting and analyzing simple research, like customer surveys or focus groups. Once they identify the source of the problem, they can use resources provided by their e-commerce platform to simplify the purchase experience. Okay, moving on. The last technique I have to optimize your e-commerce strategy is to reconsider pricing. I get it. This is definitely tricky. We learned in previous courses that to maintain a successful business, you need a good return on your investments. Meaning, it’s essential that you bring in more money to your e-commerce business than you spend. When setting the prices for your items, it may be tempting to set the value of your products at a high level. In theory, if you set your product value as high, you’ll earn more money when customers buy, right? However, high prices can turn away customers from choosing your products. I’m not saying that you should undervalue your products, but it’s important to make your product listing price reasonable for new and returning buyers. To take it one step further, you can also choose to make your product’s price competitive with other retailers. This means adjusting certain product prices so that they match or are lower than your competitors. When your products appear on the Google Shopping tab, their lower price point will help them stand out. If you decide to use this technique, makes sure that you have calculated reasonable ROI data. Remember, optimization is an ongoing part of the e-commerce industry. Make sure you consistently check in with how your optimization efforts are doing. If you notice something isn’t going the way that you would like, don’t be afraid to try a different approach.
Plan for seasonal events
- Reading Duration: 20 minutes
In an earlier reading, you learned about identifying special events and holidays for marketing and promotional opportunities. In this reading, you’ll learn Google Ads features that allow you to plan for these occasions.
During special events and holidays, e-commerce stores want an increase in conversion rates (in this case people clicking on your ads) since more people are searching to buy products online. Google Ads allows you to prepare for this by using the Performance Planner.
Performance Planner
Performance Planner is a useful tool within Google Ads that allows you to forecast your Search, Display, and Shopping campaign’s performance based on your budget. That means you can predict future outcomes of holiday and special event sales. The planner also addresses seasonality based on your business type and location.
You can review how changes to campaigns might affect overall performance and key metrics such as conversions, conversion value, or clicks.
In addition, using Performance Planner can help you:
-
Explore outcomes by adjusting campaign settings
-
Understand opportunities in seasonal periods
-
Manage budgets across accounts and campaigns
How it works
The Performance Planner tool works by using your campaign history and billions of search queries to create forecasts—or predictions—on how well your campaign will perform. The tool helps you create plans for your advertising budget.

Unlike making Smart Bidding adjustments, Performance Planner relies on existing campaigns. If your campaigns don’t have enough conversions to create a forecast, but they have enough clicks, you can manually enter a conversion rate to assess conversion forecasts.
Requirements to use the Performance Planner Tool
To use the the performance planner tool for a standard or Smart Shopping campaign, you must:
-
Have received at least 100 impressions in the last seven days
-
Have received at least 10 conversions and/or conversion values within the last 10 days
-
Have been active each day with a minimum spend of $10 USD or more in the last 10 days
Key takeaways
Google Ads takes into account the variability of seasonal and special event shopping. Using tools like the Performance Planner and Smart Bidding adjustments will help you prepare your campaigns for an increase in shopping traffic.
Resources for more information
For more information on the Google Ads tools presented in this reading, check out the following resources
-
Get your campaigns ready for the holidays: Read about the tools Google Ads offers to help you get ready for holiday advertising.
-
About Performance Planner: Read more about the features offered with the Performance Planner
Seasonal budgeting and bidding
- Reading Duration: 20 minutes
Earlier in this lesson, you learned about seasonality, the regular and predictable fluctuation of e-commerce traffic around special holidays, events, and weather on a quarterly or yearly basis. We discussed how considering seasonality can help you determine when your business will receive a potential increase or slowdown in revenue sales, which allows you to plan promotional opportunities accordingly.
You also learned about Performance Planner, a Google Ads tool that allows you to forecast your Search, Display, and Shopping campaigns’ performance based on a given budget. In this reading, you’ll learn how to evaluate data from Performance Planner to set a budget for a holiday period. You’ll also learn how to effectively adjust your bids during seasonal fluctuations in sales.
Set budgets based on business objectives
As an e-commerce analyst, you may be asked to make budget recommendations. Performance Planner and similar tools provide data visualizations that can help you analyze the data in order to make these types of recommendations.
It is important that you base your budget recommendations on business goals. For example, if maximum profit during the holiday season is your business goal, you need to determine what budget would best help you achieve that goal.
When assessing your budget for a given period, you also need to consider the law of diminishing returns. The law of diminishing returns is an economic principle stating that if investment in a particular area increases, the rate of profit from that investment will eventually decrease if other variables remain constant. So as you budget for an ad campaign, it is important to understand that your first $1,000 will probably be spent more efficiently than your next $1,000, and so on, until the point at which you are no longer gaining revenue.
The chart below illustrates that as you start to spend more, the revenue you gain for each dollar will be less. If your primary goal is to maximize your profit, you need to find the point at which your revenue minus ad spend is at its highest, or the point of diminishing returns.

In this example, your profit for a $25K ad spend is $15K, and your profit for a $30K ad spend is $14K. Therefore, spending $25K is the point of diminishing returns, as it is predicted to be more profitable than spending $30K. An ad spend of $25K would then be your recommended budget in order to hit the business objective of maximizing profit.
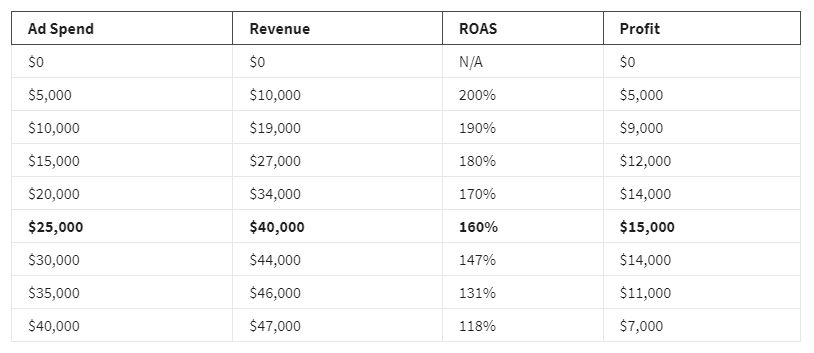
Set bids based on seasonal trends
If you’re not using an automated bidding system, you will typically base your bids on recent performance. If your goal were to drive conversions, for example, you would look at recent conversion rates and bid similarly to your bids in those campaigns. In order to calculate an amount, you can divide an average revenue-per-click by your return-on-ad-spend target. Revenue-per-click is the average revenue for each individual click on all of your pay-per-click keywords and ads. To review, return on ad spend, or ROAS, is how much revenue is gained for each dollar spent.
Let’s say you had a recent revenue-per-click of $2 and your target ROAS was 160%. You could use the following formula to determine a bid level that would help you meet that target:
(Revenue-per-click / ROAS Target = Target Bid)
($2 / 160% = $1.25)
However, there are periods throughout the year—such as around the holidays—when there is likely to be a swing in performance, and you will need to plan for these shifts. To plan effectively, you might look at year-over-year (YoY) performance to suggest how much to increase or decrease your bids by in order to make up for the projected performance shift. You can do this by comparing the previous year’s performance to the average on certain days during the holiday season and adjusting your bids accordingly. For example, if you notice that the revenue-per-click averages on Black Friday are 565% higher than the typical average, you may want to bid that much higher to maximize your revenue while achieving a similar ROAS.
Note: Seasonality adjustments in Google’s Smart Bidding can help you automatically make these types of adjustments.
One way to plan how to bid differently throughout a holiday period is to create a bid calendar like the one:

In this calendar, the different colors indicate the revenue-per-click:
-
Lower than average (red)
-
Average (yellow)
-
Somewhat above average (light blue)
-
A lot above average (blue)
-
Substantially above average (dark blue)
So, for example, if your average revenue-per-click were $2, but on Black Friday, this typically increases to $5, then you would want to increase your bids on Black Friday. You could determine how much to increase your bids by using the following formula:
((Projected Revenue-per-click − Average Revenue-per-click) / Average Revenue-per-click) x 100 = Bid Increase Percentage
(($5-$2) / $2 ) x 100 = 150%
If you’re using automated bidding, you may not need to use this type of formula across an entire holiday season. However, it’s still important for you to know when to expect increases and decreases in bids, which should lead to respective increases and decreases in ad spend and revenue on those days. With automated bidding, you may also utilize the “seasonality adjustments” feature in Google Ads, which often requires similar calculations for an expected change in conversion rates for a short period.
Key takeaways
As a digital marketer or e-commerce analyst, you will need to react to predicted shifts in performance during holiday periods and seasonal events. Tools like Performance Planner and Smart Bidding can take some of the guesswork out of projecting these shifts. It’s important to understand how to evaluate the data and most effectively adjust your budgets and bidding to help you achieve your business goals.
Activity: Set seasonal budgets and bids
- Practice Quiz. 1 question. Grade: 100%
- Access Quiz.

- On Step 1: Access the template
To use the template for this course item, click the link below and select “Use Template.”
- Link to template: Holiday budget and bid planning
Activity Exemplar: Set seasonal budgets and bids
- Reading Duration: 10 minutes
Here is a completed exemplar along with an explanation of how the exemplar fulfills the expectations for the activity.
Completed Exemplar
To review the exemplar for this course item, click the link below and select “Use Template.”
- Link to exemplar: Holiday budget and bid planning
Assessment of Exemplar
Compare the exemplar to your completed holiday budget and bid planning spreadsheet. Review your work using each of the criteria in the exemplar. What did you do well? Where can you improve? Use your answers to these questions to guide you as you continue to progress through the course.
Review the following components in the holiday budget and bid planning spreadsheet:
Budget Planning tab:
-
A formula to calculate the ROAS at different spend and revenue amounts has been added to all cells in the ROAS column of the chart.
-
A formula to calculate the profits at different spend and revenue amounts has been added to all cells in the Profits column of the chart.
-
The row in the chart that contains the point of diminishing returns has been highlighted.
-
The point of diminishing returns has been labeled on the graph.
-
The target ROAS and recommended budget have been entered in their respective cells underneath the chart.
Bidding Calendar tab:
-
Calculations to determine how much to increase or decrease bids during the holiday period have been completed, and percentages have been added to the Bid Adjustments column in the chart.
-
“Decrease,” “increase,” or “no change” has been entered next to each bid to indicate whether the bid will decrease, increase, or stay the same as the previous year’s bid.
Which seasons do you shop online the most?
- Discussion Prompt Duration: 10 minutes
Marketers have to ride the tide of seasonality, or the regular highs and lows of e-commerce traffic based on special holidays, events, or the weather.
Think about your online shopping habits and consider the following questions:
Which season or part of the year do you tend to shop online most frequently, and why?
When you shop online during this time, are you buying items for yourself or for others?
Please write 3-4 sentences (60–80 words) as a response to this prompt. Then, go to the discussion forum and, applying what you’ve learned about seasonality and seasonal marketing, comment on at least two posts from other learners.
Answer
During the holiday season, particularly in the weeks leading up to Christmas and right after, I find myself shopping online the most.
The abundance of festive promotions and attractive discounts during this period make it an ideal time to purchase gifts for friends and family.
Before Christmas, my focus is on finding the perfect presents, while post-Christmas, I take advantage of the enticing promotions to indulge in some well-deserved personal shopping, making the most of the attractive deals offered by various online retailers.
Test your knowledge: How to optimize an e-commerce businesses’ sales
- Practice Quiz. 5 questions. Grade: 100%
4. Review: Ads and campaigns in e-commerce
Wrap-up
- Video Duration: 1 minute
It’s time to review what we learned in this section of the course. You started out by discovering the benefits of online advertising. Then you learned about Google ads. You also learned how to create Smart Shopping campaigns. Next, you explored how the concept of seasonality influences e-commerce traffic, and how you’ll plan ahead by reviewing expected patterns. Then you finished up by learning how to optimize your e-commerce marketing strategies. Coming up, you’ll discover how to engage customers. First, you’ll learn how to create an engaging online experience for customers. You’ll also learn about personalization and why it’s important for e-commerce. Next, you’ll learn more about the digital checkout process and ways to improve it. You’ll learn about the shipping and delivery process that takes place after a customer places their order. Finally, you’ll also learn about how to build strong relationships with customers by providing quality customer service. Congrats on the hard work. I’m excited to stay with you on this journey as you continue to learn more about e-commerce.
Glossary terms from module 3
- Reading: Duration: 10 minutes
Module 3 challenge
- Quiz: 10 questions. Grade: 100%
- Link to challenge 1